There are many kinds of units in use in the world. For example, distance can be reported in meters, kilometers, feet, inches, etc. The agreed marking methods and the units used aim to clarify the situation. Table 1 shows the seven basic units of the SI system. All other units are based on these. [br][br]This chapter focuses on the most common units used in Finland and their multiples. Of the units in Table 1, these are length (distance), mass, and time.[br][br][color=#0000ff]If you are not familiar with SI-system, use time to learn it. It is required in your engineering studies here in Finland.[/color][br]
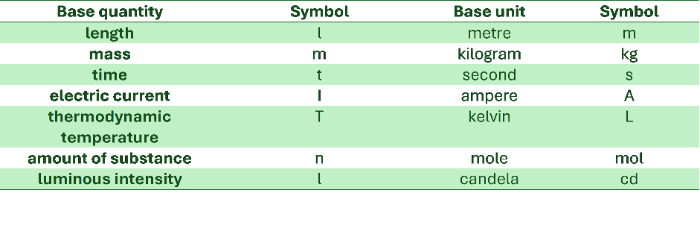
Table 1. The International System of Units
The area of a rectangle is solved as side lenght times the length of the other side. Since lengths are given in metres, the result is squared metre (m[sup]2[/sup]). In a similar way, the volume of the edge is given as a cubic metre (m[sup]3[/sup]). On the other hand, in cooking and baking, volumes are given in deciliters and liters. In the technical field, it is also easy to give a volumetric flow in the form of litres per minute. Since a litre is not a basic unit, it must be converted to cubic meters for calculations if necessary. This change can be made with a ratio[br][br][math]1\;\cal l= 1\;dm^3[/math][br][br]Table 2 lists the most common units of volume based on litres. The units used are tied up with professional field. For example, in pharmaceuticals, we talk about millilitres (ml). In brewing operations, it is more common to talk about hectolitres (hl).[br][br]
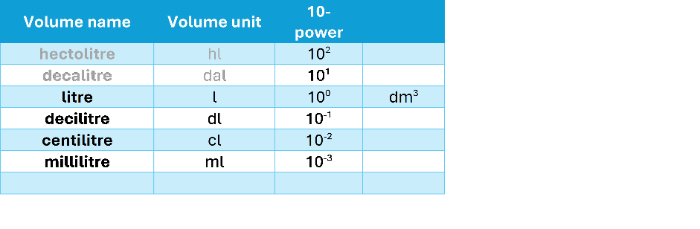
Table 2: Derivative units of volume


