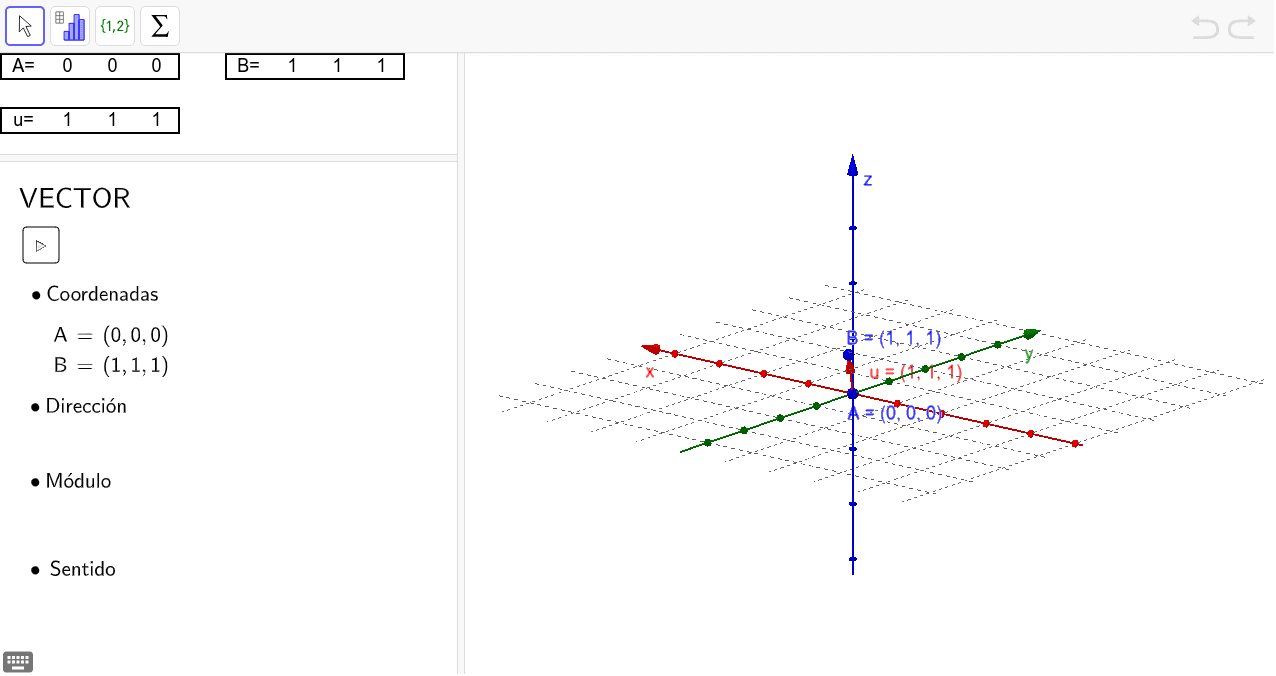
Vector
[math][/math][br][math]Un\;vector\;en\;el\;espacio\;es\;un\;segmento\;orientado\;que\;est\acute{a}\;determinado\;por\;dos\;puntos\;A\;y\;B.[/math][br][math][/math][br][list][br][*][math]M\acute{o}dulo:\: longitud\;del\;segmento\;\overline{AB}. Se\;escribe \left| \overrightarrow{AB}\right |.[/math][br][math][/math][br][*][math]Direcci\acute{o}n:\:es\;la\;recta\;sobre\;la\;que\;est\acute{a}\;situado\;el\;vector.\\Se\;dice\;que\;dos\;vectores\;tienen\;la\;misma\;direcci\acute{o}n\;si\;est\acute{a}n\;situados\;en\;la\;misma\;recta\;o\;en\;rectas\;paralelas.[/math][br][math][/math][br][*][math] Sentido:\:es\;la\;forma\;de\;recorrer\;el\;segmento\;\overline{AB},\;es\;decir,\;indicar\;cu\acute{a}l\;de\;los\;puntos\;es\;el\;origen\;y\;cu\acute{a}l\;es\;el\;extremo.[br][/math][br][/list][br][math][/math][br][math]Si\;A=(a_1,a_2,a_3)\;y\;B=(b_1,b_2,b_3)\;las\;coordenadas\;del\;vector\;\overrightarrow{AB}\;se\;calculan\;de\;la\;siguiente\;forma:[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]\:\:\:\:\:\overrightarrow{AB}=(b_1-a_1,b_2-a_2,b_3-a_3)[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]Si\;\overrightarrow{u}=(u_1,u_2,u_3)\;su\;m\acute{o}dulo\;se\;calcula\;de\;la\;siguiente\;foma:[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]\:\:\:\:\:\left|u\right|=\sqrt{u_1^2+u_2^2+u_3^2}[/math][br][math][/math]
[math] EJERCICIOS[/math][br][math][/math][br][list=1][br][*][math]Escribe\;las\;coordenadas\;de\;los\;puntos\;A=(-2,3,4)\;y\;B=(5,-1,6).\;¿Cu\acute{a}les\;son\;las\;coordenadas\;del\;vector\;\overrightarrow{AB}?[/math][br][math][/math][br][*][math]Considera\;los\;puntos\;A=(2,5,4)\;y\;B=(3,7,1).[/math][br][list=a][br][*][math]Halla\;las\;coordenadas\;del\;vector\;\overrightarrow{AB}.[/math][br][*][math]Halla\;las\;coordenadas\;del\;vector\;\overrightarrow{BA}.[/math][br][*][math]Indica\;las\;similitudes\;y\;diferencias\;entre\;los\;vectores\;\overrightarrow{AB}\;y\;\overrightarrow{BA}.[/math][br][/list][br][math][/math][br][*][math]Sean\;el\;vector\;\overrightarrow{AB}=(-3,5,2)\;y\;el\;origen\;A=(0,-2,1).\;Halla\;el\;extremo\;B.[/math][br][math][/math][br][*][math]Sean\;el\;vector\;\overrightarrow{AB}=(2,1,-4)\;y\;el\;extremo\;B=(-7,4,0).\;Halla\;el\;origen\;A.[/math][br][math][/math][br][*][math]Halla\;el\;m\acute{o}dulo\;del\;vector\;\overrightarrow{u}=(-2,8,3).[/math][br][math][/math][br][*][math]Halla\;el\;m\acute{o}dulo\;del\;vector\;\overrightarrow{AB}\;siendo\;A=(-3,5,-2)\;y\;B=(9,-5,1).[/math][br][/list][br][math][/math]
Ecuaciones de la recta
[math][/math][br][math]Una\;recta\;en\;el\;espacio\;queda\;determinada\;por:[/math][br][list][br][*][math]Un\;punto\;P\;de\;la\;recta\;donde\;el\;vector\;\overrightarrow{OP}\;se\;llama\;\textbf{vector de posición}.[/math][br][*][math]Un\;vector\;\overrightarrow{u}\;cuya\;direcci\acute{o}n\;es\;la\;recta\;y\;se\;denomina\;\textbf{vector director}.[/math][br][/list][br][math]Sean\;X=(x,y,z)\;un\;punto\;gen\acute{e}rico,\;P=(x_0,y_0,z_0)\;un\;punto\;concreto\;y\;\overrightarrow{u}=(u_1,u_2,u_3)\;un\;vector\;director.[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]1.\:Ecuaci\acute{o}n\;vectorial[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]\:\:\:\:\:(x,y,z)=(x_0,y_0,z_0)+\lambda \cdot (u_1,u_2,u_3)[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]2.\:Ecuaciones\;param\acute{e}tricas[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]\:\:\:\:\: \left.\begin{matrix}[br]x=x_0+\lambda \cdot u_1\\ [br]y=y_0+\lambda \cdot u_2\\[br]z=z_0+\lambda \cdot u_3 [br]\end{matrix}\right\}[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]3.\:Ecuaci\acute{o}n\;continua[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]\:\:\:\:\:\frac{x-x_0}{u_1}=\frac{y-y_0}{u_2}=\frac{z-z_0}{u_3}[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]4.\:Ecuaciones\;generales\;o\;impl\acute{i}citas[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]Se\;pueden\;multiplicar\;las\;razones\;de\;la\;ecuaci\acute{o}n\;continua\;dos\;a\;dos\;y\;se\;agrupan\;los\;t\acute{e}rminos\;en\;un\;miembro.[/math][br][math][/math][br][math]\:\:\:\:\: \left.\begin{matrix}[br]A \cdot x+B \cdot y+C \cdot z+D=0\\ [br]A' \cdot x+B' \cdot y+C' \cdot z+D'=0\end{matrix}\right\}[/math][br][math][/math]