SCALE FACTORS AND SCALE DRAWING
Instructions
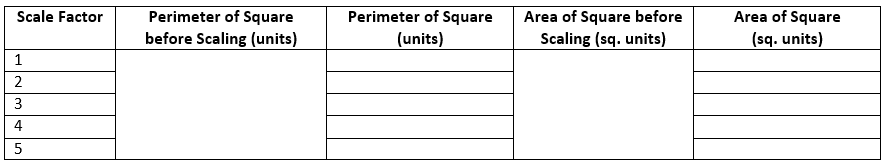
[color=#000000][b][i]CHANGE THE SCALE – WHAT HAPPENS TO AREA AND PERIMETER?[/i][/b][br][br][b]Introduction[br][/b]If we enlarge or shrink a shape, what happens to the resulting area and the perimeter? In this experiment, you will change the size of a square by adjusting a [i][b]scale factor[/b][/i]. The scale factor determines by how much you want to increase the dimensions of a starting shape – double? …triple? …etc.[br][br][b]Step 1[/b][br]Use the Distance or Length [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_distance.png[/icon]and Area [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_area.png[/icon] tools to label the perimeter and area of the green square. [br][br]Use the Move tool [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_move.png[/icon] to drag the measurement labels to new locations if they get in your way.[br][br][b]Step 2[br][/b]Use the Scale Factor slider [icon]https://tube.geogebra.org/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_slider.png[/icon] to choose how much to enlarge the green square. [br][br]Complete a Data Table like the one pictured below.[br][br][b]Step 3[/b][br]a) As the square doubles, triples, etc. in size compared to its original size, what happens to square’s perimeter?[br] [br] [br]b) As the square doubles, triples, etc. in size compared to its original size, what happens to square’s area?[br] [br] [br] [br][b]Conclusion[/b][br]What is the relationship between scale factor and perimeter?[br] [br] [br] [br]What is the relationship between scale factor and area? [br] [br] [br] [br]If a square is scaled by a factor of 7, explain how you could determine the square’s[br]perimeter and area. [br][br][br][br]Is this just unique to squares? Experiment with other polygons to find out.[br][br][/color]
