Intro To 3-D Geometry
Intro To 3-D Geometry
Prisms Overview
[b]A [u]prism[/u] is a solid object with:[/b][br][list][*]identical ends[/*][*]flat faces[/*][*]and the same [b][url=https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/cross-sections.html]cross section[/url][/b] all along its length![/*][/list][br]A [b]cross section[/b] is the shape made by cutting straight across an object.[br][img width=173,height=186]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/prism-cross-section.jpg[/img][br]The cross section of this object is a [b]triangle[/b] ...[br].. it has the same cross section all along its length ...[br]... so it's a [b]triangular prism.[br][br][br][b][b][u]Bases[/u]: [/b]The ends of a prism are parallel [br]and each one is called a base.[/b][br][br] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/bases.svg[/img] [br][br][b][b][u]Sides:[/u] [/b]The side faces of a prism are [url=https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/parallelogram.html]parallelograms[/url] [br](4-sided shapes with opposite sides parallel)[br][/b][br] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/prism-sides-small.svg[/img] [br][/b][size=100][size=150][b][u][size=200]These are all Prisms:[/size][/u][br][br][/b][/size][/size][b]Rectangular Prism: [/b] [b]Cross-Section:[br][/b][size=100][size=150][b][br][img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cuboid.svg[/img] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/square.svg[/img][br][br]Cube: Cross-Section:[br][br][img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cube.svg[/img] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/square.svg[/img][br][br]Triangular Prism: Cross-Section:[br][br][img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/tri-prism.svg[/img] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/triangle.svg[/img][br][br]Pentagonal Prism: Cross-Section:[br][br][img width=175,height=106]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/pentagonal-prism.png[/img] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/pentagon.svg[/img][br][br][br][size=200][u]Regular and Irregular Prisms:[/u][br][/size][br]All the previous examples are [b]Regular[/b] Prisms, because the cross section is regular (in other words it is a shape with equal edge lengths, and equal angles.)[br]Here is an example of an [b]Irregular Prism[/b]:[br][table][tr][td]Irregular Pentagonal Prism:[/td][td] [/td][td] [b][table][tr][td]Cross-Section:[/td][/tr][/table][br][/b][/td][/tr][tr][td][br][img width=181,height=119]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/irr-pentagonal-prism.png[/img][/td][td] [/td][td][img width=141,height=110]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/irregular-pentagon.png[/img][/td][/tr][tr][td][br][/td][td][/td][/tr][tr][td]It is "irregular" because the [br]cross-section is not "regular" in shape.[/td][/tr][/table][br][/b][/size][/size][br][b][u][size=150][size=200]Surface Area of a Prism:[br][/size][br][/size][/u][/b][br] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/prism-area-perimeter.svg[/img][br] [br][b]Surface Area = 2 × Base Area + Base Perimeter × Length[br][/b][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] What is the surface area of a prism where the base area is 25 m[sup]2[/sup], the base perimeter is 24 m, and the length is 12 m: [br][br]Surface Area= 2 × Base Area + Base Perimeter × Length[br] = 2 × 25 m[sup]2[/sup] + 24 m × 12 m[br] = 50 m[sup]2[/sup] + 288 m[sup]2[/sup][br] = [b]338 m[sup]2[/sup][/b][b][sup][br][/sup][/b][br]Use the area calculation tool to find the area of bases: https://www.mathsisfun.com/area-calculation-tool.html[br][br][size=200][b][u]Volume of a Prism:[/u][/b][br][/size][br]The Volume of a prism is the area of one end times the length of the prism.[br][br] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/prism-area-perimeter.svg[/img][br][b]Volume = Base Area × Length[/b][br][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] What is the volume of a prism where the base area is 25 m[sup]2[/sup] and which is 12 m long:[br][br]Volume= Area × Length[br] = 25 m[sup]2[/sup] × 12 m[br] = [b]300 m[sup]3[/sup][/b]
Cylinders - Overview
Cylinders - Overview
[b][size=150][u][size=200]Cylinder Facts:[br][/size][/u][/size][/b][br] [img width=180,height=157]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cylinder-shiny.jpg[/img][br][br][b]Notice these interesting things:[/b][br][list][*]It has a flat base and a flat top[/*][*]The base is the same as the top[/*][*]From base to top the shape stays the same[/*][*]It has one curved side[/*][*]The cross-section of a cylinder is a circle[/*][/list][br][img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cylinder-cross-section.svg[/img][br][br] [br]An object shaped like a cylinder is said to be [b]cylindrical.[br][/b][br] [br] [img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cylinder-dimensions.svg[/img][br][br][br][b][u][size=200]Surface Area of a Cylinder:[/size][br][br][/u][/b]The Surface Area has these parts:[br][list][*][i]Surface Area of Both Ends[/i] = 2 × π × r[sup]2[/sup][/*][*][i]Surface Area of Side[/i] = 2 × π × r × h[/*][/list][br]Which together make:[br][b]Surface Area = 2 × π × r × (r+h)[/b][br][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] h = 7 and r = 2 [br][br]Surface Area= 2 × π × r × (r+h)[br] = 2 × π × 2 × (2+7)[br] = 2 × π × 2 × 9[br] = 36 π[br] ≈ [b]113.097[br][/b][br][b][u][size=200]Volume of a Cylinder:[/size][br][br][/u][/b]To calculate the volume we multiply the area of the base by the height of the cylinder:[br][list][*]Area of the base: π × r[sup]2[/sup][/*][*]Height: h[/*][/list][br]And we get:[br][b]Volume = π × r[sup]2 [/sup]× h[br][/b][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] h = 7 and r = 2[br][br]Volume= π × r[sup]2[/sup] [sup][/sup]× h[br] = π × 2[sup]2[/sup] [sup][/sup]× 7[br] = 28 π[br] ≈[b] 87.96[/b][br][br][b][u][size=200]Volume = pizza[/size][/u][/b][br]How to remember: [b]Volume = pizza[/b][img]https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cylinder-pizza.svg[/img][br]Imagine you just cooked a [b]pizza[/b].[br]The radius is "z", and the thickness "a" is the same everywhere ... what is the volume?[br][b]Volume = [/b][b]pi[/b] × [b]z[/b] × [b]z[/b] × [b]a[/b][br](we would normally write "pi" as π, and [b]z[/b] × [b]z[/b] as [b]z[sup]2[/sup][/b], but you get the idea!)
Cones - Overview
[br][img width=170,height=193]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-shiny.jpg[/img][br][br][size=200][b][u]Cone Facts:[br][/u][/b][/size][br][b]Notice these interesting things:[/b][br][list][*]It has a flat base[/*][*]It has one curved side[/*][/list][br] [br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-apex-base.svg[/img][br] [br][list][*]The pointy end of a cone is called the [b]apex[/b][/*][*]The flat part is the [b]base[/b][/*][*]An object shaped like a cone is said to be [b]conical[/b][/*][/list][br][b][u][size=200]Surface Area of a Cone:[br][/size][/u][/b][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-dimensions.svg[/img][br][br]The Surface Area has two parts:[br][list][*]The [i]Base Area [/i]= π × r[sup]2[/sup][/*][*]The [i]Side Area[/i] = π × r × s[/*][/list][br]Which together makes:[br][b]Surface Area = π × r × (r + s)[/b][br]Note: we can calculate [b]s = √(r[sup]2[/sup]+h[sup]2[/sup])[br][/b][br][b][u]Example: [/u][/b]h = 7 and r = 2[br][br]Surface Area of Base= π × r[sup]2[/sup][br] = π × 2[sup]2[/sup][br] = 4π[br] ≈ [b]12.57[/b][br] [br]Surface Area of Side= π × r × √(r[sup]2[/sup]+h[sup]2[/sup])[br] = π × 2 × √(2[sup]2[/sup]+7[sup]2[/sup])[br] = π × 2 × √(4+49)[br] = 2π√(53)[br] ≈ [b]45.74[br][/b][br]Total Surface Area ≈ 12.57 + 45.74 ≈ [b]58.31[br][br][/b][br][b][u][size=200]Volume of a Cone:[/size][/u][/b][br][br][b]Volume = 1/3 π × r[sup]2 [/sup]× h[/b][br][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] h = 7 and r = 2[br][br]Volume= 13 π × r[sup]2[/sup] [sup][/sup]× h[br] = 13 π × 2[sup]2[/sup] [sup][/sup]× 7[br] = 283 π[br] ≈ [b]29.32[br][br][br][u][size=200]Volume of a Cone vs Cylinder:[br][/size][/u][/b][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-vs-cylinder.svg[/img][br][br]The volume formulas for cones and [url=http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/cylinder.html]cylinders[/url] are very similar:[br][br][table][tr][td]The volume of a cylinder is: [/td][td]π × r[sup]2 [/sup]× h[/td][/tr][tr][td]The volume of a cone is: [/td][td]1/3 π × r[sup]2 [/sup]× h[/td][/tr][/table][br][b]So a cone's volume is exactly one third ( 13 ) of a cylinder's volume.[br][/b][br][br][b][u][size=200]Different Shaped Cones:[/size][/u][/b][br][br][img width=127,height=220]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-wood1.jpg[/img][img width=173,height=220]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-wood3.jpg[/img][img width=199,height=220]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-wood4.jpg[/img][br][br][b]Construction Cone[br][/b][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/cone-construction.svg[/img][br]This is [i][b]almost[/b][/i] a cone, but the top is chopped off (called a "truncated cone").[br]Also it has a wider base added so it doesn't fall over![br]
Spheres Overview
[u][size=200][b]Sphere Facts[/b][br][/size][/u][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-radius.svg[/img][br][b]Notice these interesting things:[/b][br][list][*]It is perfectly symmetrical[/*][*]All points on the surface are the [br]same distance [b]"r"[/b] from the center[/*][*]It has [b]no[/b] edges or [br]vertices (corners)[/*][*]It has one [b]surface[/b] [br](not a "face" as it isn't flat)[/*][/list][br] [img width=304,height=299]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-glass.jpg[/img][i][br][/i][i]Glass Sphere[/i]. [br]Balls and marbles are shaped like spheres.[br][br][b][u][size=200]Largest Volume for Smallest Surface:[br][/size][/u][/b][br]Of all the shapes, a sphere has the smallest surface area for a volume. Or put another way it can contain the greatest volume for a fixed surface area.[br][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] if you blow up a balloon it naturally forms a sphere because it is trying to hold as much air as possible with as small a surface as possible[br] [br][b][u][size=200]In Nature[br][img width=200,height=193]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/bubble.jpg[/img][br][/size][/u][/b]The sphere appears in nature when a surface wants to be as small as possible. [b]Examples[/b] include bubbles and water drops. Can you think of more?[br][br][table][tr][td][b][u]The Earth:[br][/u][/b]The Planet Earth, our home, is [i]nearly[/i] a sphere, except that it is squashed a little at the poles.[br][/td][td][img width=162,height=162]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/planet-earth.jpg[/img][/td][td][br]It is a [b]spheroid[/b], which means it just misses out on being a sphere because it isn't perfect in one direction (in the Earth's case: North-South)[/td][/tr][/table][br][b][u][size=200]Volume and Surface Area[/size][/u][/b][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-radius.svg[/img][br][b]Surface Area = 4 × [i]π[/i] × r[sup]2[br][/sup][/b][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] r = 5[br][br]Surface Area= 4 × π × r[sup]2[/sup][br] = 4 × π × 5[sup]2[/sup][br] = 4 × π × 25[br] = 100 π[br] ≈ 314[br] [br][b]Volume = (4/3) × [i]π[/i] × r[sup]3[br][/sup][/b][br][b][u]Example:[/u][/b] r = 5[br][br]Volume= (4/3) × π × r[sup]3[/sup][br] = (4/3) × π × 5[sup]3[/sup][br] = (4/3) × π × 125[br] ≈ 524[br][br][size=200][b][u]Hemisphere[br][/u][/b][br][/size][img width=221,height=287]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/hemisphere.jpg[/img][br]A hemisphere is an exact half of a sphere.[br][br][b][u][size=200]Other Cool Spheres[br][/size][/u][/b][br][img width=301,height=250]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-crystal.jpg[/img][img width=190,height=192]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/marble.jpg[/img][br][table][tr][td][img width=173,height=178]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-jade.jpg[/img][/td][td][img width=171,height=178]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-check.jpg[/img][/td][/tr][tr][td][img width=166,height=178]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-dark.jpg[/img][/td][td][img width=171,height=178]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/sphere-brass.jpg[/img][br][br][/td][/tr][/table]
Pyramids Overview
When we think of pyramids we think of the [b]Great Pyramids of Egypt[/b].[br]They are actually [i][b]Square Pyramids[/b][/i], because their base is a Square.[br][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/pyramids.jpg[/img][br][img width=220,height=148]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/pyramid-outlined.jpg[/img] [br][br][br][b][u][size=200]Parts of a Pyramid[/size][/u][/b][br][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/pyramid-defined.svg[/img] [br][br]A pyramid is made by connecting a [b]base[/b] to an [b]apex[/b][br]The base is a polygon (flat with straight edges) and all other faces are triangles. No curves![br][br][br][b][u][size=200]Types of Pyramids[br][/size][/u][/b][br]There are many types of Pyramids, and [u]they are named after the shape of their base[/u].[br]- Triangular Pyramid[br]-Square Pyramid[br]-Pentagonal Pyramid[b][i][br]... and so on ...[br][br][br][br][/i][/b][b][u][size=200]Surface Area and Volume[/size][/u][/b][br][br][img]http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/images/pyramid-height-perimeter.svg[/img][br][u]The Volume of a Pyramid[/u] [br] [br][b]Volume = [sup]1[/sup]/[sub]3[/sub] × [Base Area] × Height[/b] [br][br][b][u]The Surface Area of a Pyramid[br][br][/u][/b] [b]Surface Area = [Base Area] + [sup]1[/sup]/[sub]2[/sub] × Perimeter × [Slant Length][/b][br][br]
Composite Figures Overview
A [b]composite solid[/b] is a figure that is made up of [b]more than one[/b] solid.[br][br][img]https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat2793-volumeofcompositeshapes100-slideshare-120801103756-phpapp01/95/mat2793-volume-of-composite-shapes-6-728.jpg?cb=1344313041[/img][br][br][b][u][size=200]Surface Area:[/size][/u][/b]
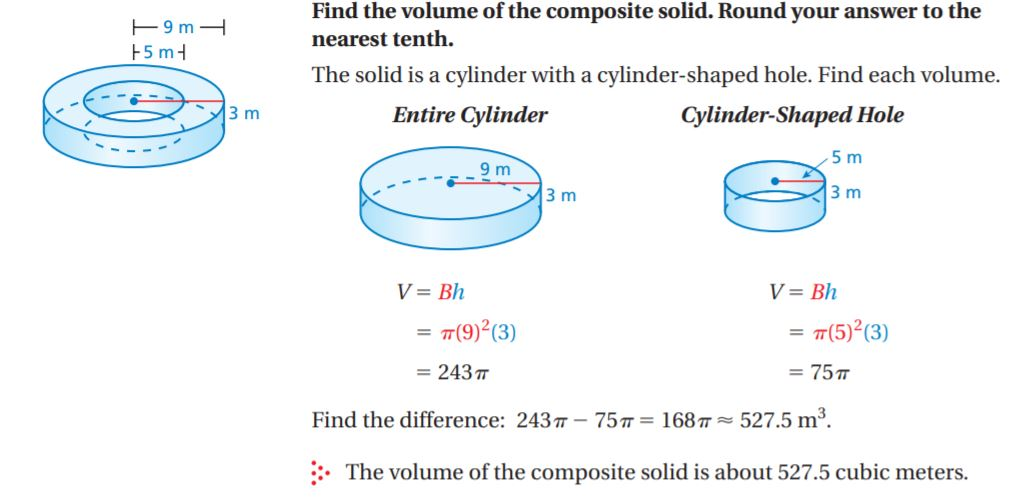
Example:

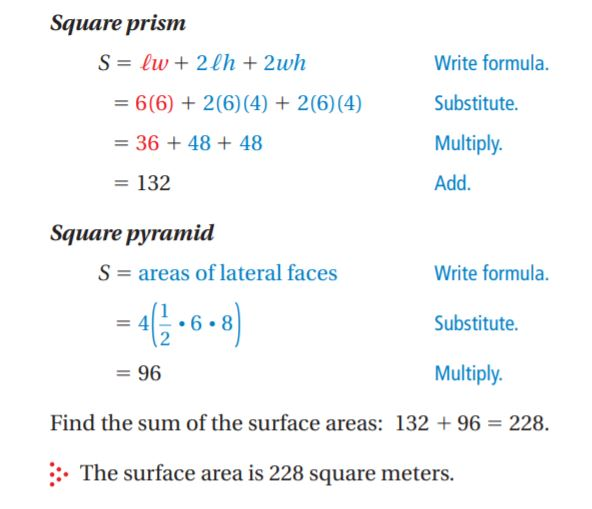
[b][u][size=200]Volume:[/size][/u][/b]
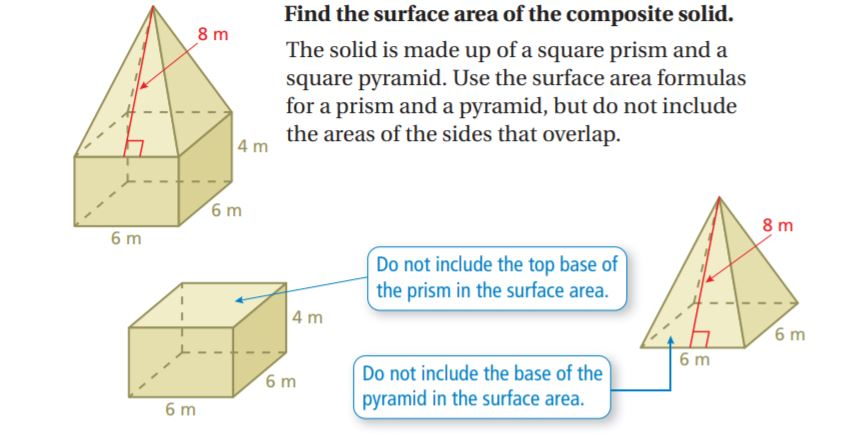
Example:
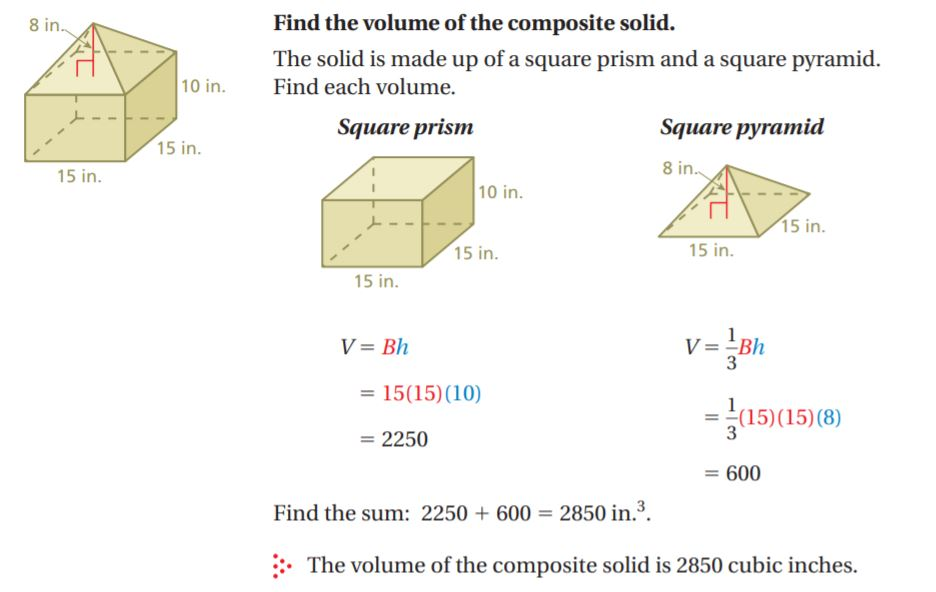
Example: