Pengenalan
[b][size=150][size=200][color=#0000ff]What is Linear Kinematic Motion?[/color][/size][/size][/b][size=100][justify][size=150]Linear kinematic motion refers to the study of the [i]movement of objects along a straight line[/i], describing how their position, velocity, and acceleration change over time. This concept is fundamental in understanding motion in physics and is widely applied in various real-world situations, such as driving a car, objects falling freely under gravity, or the motion of projectiles.[/size][br][br][size=150][/size][size=150]Kinematics focuses on describing the motion of an object without considering the forces that cause it. In linear motion, we are particularly interested in how the following quantities interact:[br][/size][/justify][list=1][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Displacement (s):[/i][/b] The distance and direction of an object's movement from its initial position.[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Velocity (v):[/i][/b] The speed of the object in a specific direction. It can be initial velocity (u) or final velocity (v).[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Acceleration (a):[/i][/b] The rate at which the velocity changes over time.[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Time (t):[/i][/b] The duration of the motion.[br][/size][/size][/*][/list][size=200][b][color=#0000ff]Apakah Gerakan Kinematik Linear?[/color][/b][/size][br][size=150]Pergerakan kinematik linear merujuk kepada kajian pergerakan objek sepanjang garis lurus, menerangkan bagaimana kedudukan, halaju, dan pecutannya berubah mengikut masa. Konsep ini adalah asas dalam memahami gerakan dalam fizik dan digunakan secara meluas dalam pelbagai situasi dunia sebenar, seperti memandu kereta, objek jatuh bebas di bawah graviti, atau gerakan peluru.[br][br]Kinematik memberi tumpuan kepada menerangkan pergerakan objek tanpa mengambil kira daya yang menyebabkannya. Dalam gerakan linear, kami amat berminat dengan cara kuantiti berikut berinteraksi:[br] [br][list=1][*][b][i]Sesaran (s):[/i][/b] Jarak dan arah pergerakan objek dari kedudukan asalnya.[/*][*][b][i]Halahu (v): [/i][/b]Kelajuan objek dalam arah tertentu. Ia boleh menjadi halaju awal (u) atau halaju akhir (v).[/*][*][b][i]Pecutan (a):[/i][/b] Kadar di mana halaju berubah mengikut masa.[/*][*][b][i]Masa (t):[/i][/b] Tempoh pergerakan.[/*][/list][/size][/size]


CONTOH 3
[size=150]A particle moves along a straight line and passes through a fixed point [i]O[/i]. Its velocity, [br][i]v[/i] ms[sup]-1[/sup], [i]t[/i] seconds after passing through the point [i]O [/i]is given by [math]v=3t-12[/math].[br][i]Suatu zarah bergerak di sepanjang satu garis lurus dan melalui satu titik tetap O. Halaju, dalam ms[sup]-1[/sup], zarah itu pada masa t saat selepas melalui titk O diberi oleh [/i][math]v=3t-12[/math][br][br](a) Calculate[br] [i]Hitung[/i][br] (i) the initial velocity of the particle,[br] [i] halaju awal, dalam ms[sup]-1[/sup][/i][br] (ii) the instantaneous velocity, in ms[sup]-1[/sup], of the particle when [i]t=5[/i],[br] [i]halaju seketika, dalam ms[sup]-1[/sup][/i][br] (iii) the time, in seconds, when the instantaneous velocity, in ms[sup]-1[/sup], of the particle is 6ms[sup]-1[/sup].[br] [i]masa, dalam saat, apabila halaju seketika zarah itu ialah 6ms[/i][sup][i]-1[/i][br][/sup][br][br][b]Solution/Penyelesaian:[/b][/size]
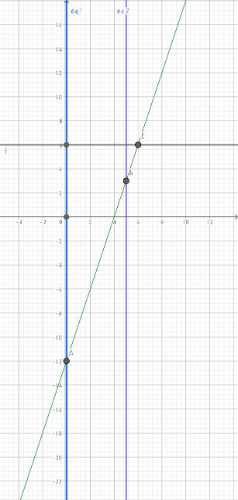

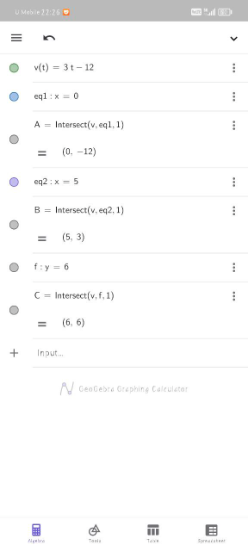
(a)(i) Hence, the initial velocity of the particle is -12ms[sup]-1[/sup].[br] [i]Maka, halaju awal zarah itu ialah -12 ms[sup]-1[/sup].[br][/i][br] (ii) Hence, the instantaneous velocity of the particle when [i]t=5 [/i]is 3ms[sup]-1[/sup].[br] [i] Maka, halaju seketika zarah itu apabila t=5 ialah 3ms[sup]-1 [/sup].[sup] [/sup][br][/i][br] (iii) Hence, the time is 6 seconds when the instantaneous velocity of the particle is 6ms[sup]-1[/sup]. [br][i] Maka, masa ialah 6 saat apabila halaju seketika zarah itu ialah 6ms[sup]-1[/sup] . [/i]
[size=150](b) Sketch the velocity-time graph to represent the movement of the particle for [math]0\le t\le6[/math].[br][/size] [size=150][i]Lakarkan graf halaju-masa bagi mewakili pergerakan zarah itu untuk [math]0\le t\le6[/math][/i][/size].
EXAMPLE 6

[b]A particle moves along a straight line. At time t seconds after it starts moving,its displacement, s m, from a fixed point O is given by s = 3 + 2t – t[/b][sup]2[/sup][b] , where t is time,in seconds.[/b][size=150][size=100][b]a) Determine the velocity function, v, and acceleration function, a, of the particle.[/b][/size][size=150][size=150][size=100][b]b) On the same diagram, sketch a graph of function s, v and a for [/b][b][b][size=150]0≤ t ≤3 [/size][/b][/b][b]and explain the motion of the particle from point O for that interval.[/b][/size][/size][/size][/size]
[b]Solution[/b][br][size=100][size=150][sup][size=150][/size][/sup][/size][/size][size=150][sup][size=150]a) [/size][/sup][/size]
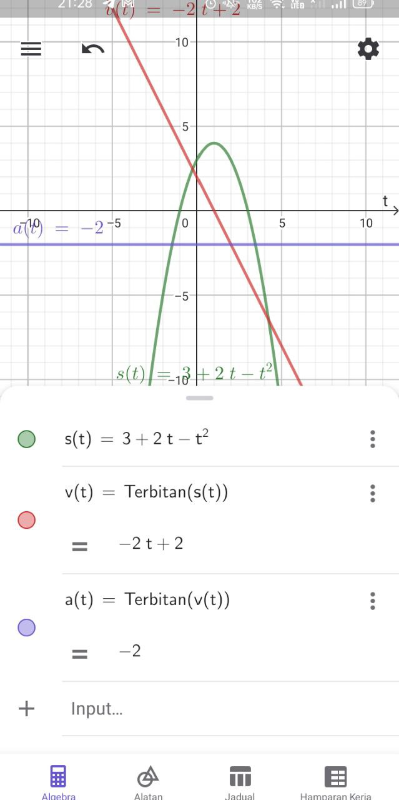
[size=100][br]Hence, the velocity function at time t , v=2-2t and acceleration function at time t ,a=-2ms[sup]-2[/sup][/size][sup][size=100][i][sup][br][br][/sup][/i][/size][/sup]b)
[size=150][size=100][size=150]Graph of the displacement, velocity, and acceleration functions of a particle that moves from the the fixed point O can be simplified on a number line as follows:[/size][/size][/size]
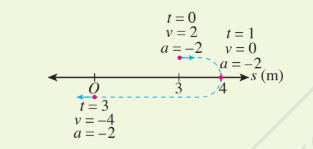
[justify][size=100]From the graph and the number line:[br][/size][/justify][list][*][size=100]It is found that the displacement of the particle at t=0 from the fixed point O is 3m, the initial velocity is 2ms[sup]-1[/sup] and acceleration is -2ms[sup]-2[/sup]. [/size][/*][*][size=100]At t=1, the particle changes its direction of motion, the displacement from the fixed point O is maximum, which is 4 m, the velocity is 0 ms[sup]-1[/sup] and the acceleration is −2 ms[sup]-2[/sup]. [/size][/*][*]At t=3, the particle reaches to the fixed point O where its displacement is 0 m, velocity is −2 ms[sup]-1[/sup], and its acceleration is the same, which is −2 ms[sup]-2[/sup]. [/*][*][size=100]The total distance traveled by the particle from t=0 to t = 3 is (4−3)+4=5 m. [/size][/*][/list]
