Pengenalan
[b][size=150][size=200][color=#0000ff]What is Linear Kinematic Motion?[/color][/size][/size][/b][size=100][justify][size=150]Linear kinematic motion refers to the study of the [i]movement of objects along a straight line[/i], describing how their position, velocity, and acceleration change over time. This concept is fundamental in understanding motion in physics and is widely applied in various real-world situations, such as driving a car, objects falling freely under gravity, or the motion of projectiles.[/size][br][br][size=150][/size][size=150]Kinematics focuses on describing the motion of an object without considering the forces that cause it. In linear motion, we are particularly interested in how the following quantities interact:[br][/size][/justify][list=1][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Displacement (s):[/i][/b] The distance and direction of an object's movement from its initial position.[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Velocity (v):[/i][/b] The speed of the object in a specific direction. It can be initial velocity (u) or final velocity (v).[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Acceleration (a):[/i][/b] The rate at which the velocity changes over time.[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Time (t):[/i][/b] The duration of the motion.[br][/size][/size][/*][/list][size=200][b][color=#0000ff]Apakah Gerakan Kinematik Linear?[/color][/b][/size][br][size=150]Pergerakan kinematik linear merujuk kepada kajian pergerakan objek sepanjang garis lurus, menerangkan bagaimana kedudukan, halaju, dan pecutannya berubah mengikut masa. Konsep ini adalah asas dalam memahami gerakan dalam fizik dan digunakan secara meluas dalam pelbagai situasi dunia sebenar, seperti memandu kereta, objek jatuh bebas di bawah graviti, atau gerakan peluru.[br][br]Kinematik memberi tumpuan kepada menerangkan pergerakan objek tanpa mengambil kira daya yang menyebabkannya. Dalam gerakan linear, kami amat berminat dengan cara kuantiti berikut berinteraksi:[br] [br][list=1][*][b][i]Sesaran (s):[/i][/b] Jarak dan arah pergerakan objek dari kedudukan asalnya.[/*][*][b][i]Halahu (v): [/i][/b]Kelajuan objek dalam arah tertentu. Ia boleh menjadi halaju awal (u) atau halaju akhir (v).[/*][*][b][i]Pecutan (a):[/i][/b] Kadar di mana halaju berubah mengikut masa.[/*][*][b][i]Masa (t):[/i][/b] Tempoh pergerakan.[/*][/list][/size][/size]


8.1 Sesaran, Halaju dan Pecutan Sebagai Fungsi Masa

[size=200][b][color=#0000ff]What is displacement?[br][/color][/b][/size][b][color=#0000ff][size=200][i]Apakah sesaran?[/i][/size][br][/color][/b][br][size=150][b]Displacement (s)[/b] of a particle and a fixed point is the distance between the particle and the nearest fixed point measured in a certain direction.[br][i][b]Sesaran (s)[/b] bagi zarah adalah jarak antara zarah itu dengan satu titik tetap, diukur dalam arah tertentu.[br][br][/i][/size][i][color=#1e84cc][size=150][b]Here is a simpler and easier to understand way to explain the displacement, velocity and acceleration based on the direction of motion of the particle relative to the fixed point O: [/b][/size][br][/color][/i][size=150][color=#1e84cc]Berikut adalah cara yang lebih ringkas dan mudah difahami untuk menjelaskan sesaran, halaju dan pecutan berdasarkan arah gerakan zarah relatif kepada titik tetap O:[br][br][/color][/size][size=150][color=#ff0000][b]Displacement:[br][/b][b]Sesaran:[/b][/color][/size][size=150][list][*][size=150][b]Negative displacement[b] (s<0)[/b]: The particle is to the left of point O.[/b][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Sesaran negatif (s<0)[/b]: Zarah berada di [b]sebelah kiri titik O[/b].[br][br][/i][list][*][size=150][b]Zero displacement[b] (s=0): The particle is exactly at point O.[/b][/b][i][br][/i][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Sesaran sifar (s=0)[/b]: Zarah berada [b]tepat di titik O[/b].[br][/i][br][list][*][size=150][b]Positive displacement (s>0): The particle is to the right of point O.[/b][br][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Sesaran positif (s>0)[/b]: Zarah berada di [b]sebelah kanan titik O.[br][br][br][/b][/i][/size][justify][color=#ff0000][b][/b][size=150][b]Velocity:[br][/b][b]Halaju:[/b][/size][b][/b][/color][/justify][size=150][i][list][*][size=150][b]Negative velocity[b] (v<0)[/b]: The particle moves to the left.[/b][/size][/*][/list] [b]Halaju negatif (v<0)[/b][i]: [/i]Zarah bergerak [b]ke arah kiri[/b][i].[br][br][/i][list][*][size=150][b]Zero [b]velocity [/b][b](v=0): Zarah berada dalam keadaan [b]pegun[/b] (tidak bergerak).[/b][/b][i][br][/i][/size][/*][/list] [b][i][i][b]Halaju [/b][/i][/i]sifar (v=0)[/b][i]: [/i]The particle is [b]at rest (not moving)[/b][i].[br][/i][br][list][*][size=150][b]Positive velocity (v>0): Zarah bergerak ke arah kanan[/b][br][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Halaju positif (v>0)[/b]: Zarah bergerak [b]ke arah kanan.[br][br][br][/b][/i][/i][/size][size=150][color=#ff0000][b]Acceleration:[br][/b][b][i]Pecutan[/i]:[br][/b][/color][/size][i][list][*][b][size=150]Negative acceleration[b] (a<0)[/b]: The particle's velocity is [b]increasing[/b] over time (the particle is speeding up).[/size][/b][/*][/list][size=150] [b]Pecutan negatif (v<0)[/b][i]: [/i]Halaju zarah [b]berkurang[/b] dengan masa (zarah semakin perlahan).[list][*][b]Zero [b]acceleration[/b][b](v=0): The particle's velocity is [b]constant[/b] (either at its maximum or minimum).[/b][/b][i][br][/i][/*][/list] [b][i][size=150][b]Pecutan [/b][/size][/i]sifar (v=0)[/b][i]: [/i]Halaju zarah adalah [b]tetap[/b] (maksimum atau minimum).[br][/size][/i][i][size=150][br][list][*][i][size=150][b]Positive acceleration[b] (a>0)[/b]: The particle's velocity is [b]decreasing[/b] over time (the particle is slowing down). [/b][/size][/i][/*][/list][/size][/i][i][size=150][b] Pecutan positif (a>0)[/b][i]: [/i]Halaju zarah [b]meningkat[/b] dengan masa (zarah semakin laju).[/size][/i]
8.2 Pembezaan dalam Kinematik Gerakan Linear
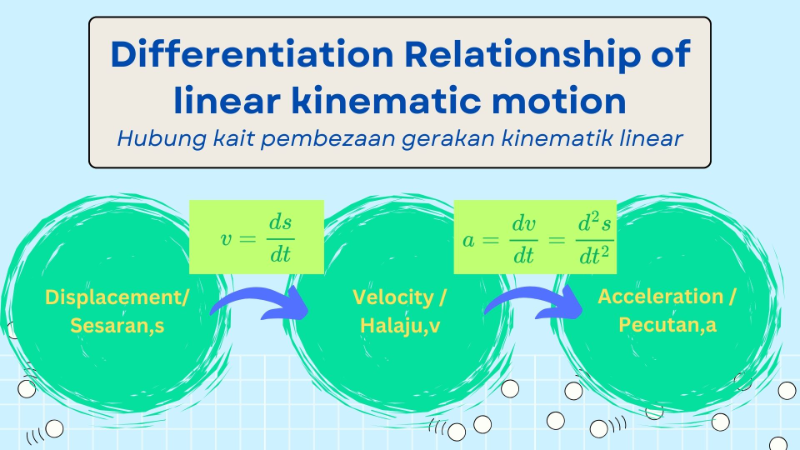
[justify][size=100]Differentiation in linear kinetic motion refers to the mathematical process of determining the rate of change of motion-related quantities, such as displacement, velocity, and acceleration, with respect to time. These rates are foundational in understanding the dynamics of objects in linear motion.[b] The differentiation always starts from displacement, s=f(x). [br][/b][i]Pembezaan dalam gerakan kinetik linear merujuk kepada proses matematik untuk menentukan kadar perubahan kuantiti yang berkaitan dengan gerakan, seperti sesaran, halaju, dan pecutan, berkenaan dengan masa. Kadar perubahan ini adalah asas dalam memahami dinamik objek dalam gerakan linear. Proses pembezaan ini sentiasa bermula dari sesaran, s = f(x).[/i][/size][i][size=100][br][br][/size][/i]The [b]velocity[/b] is defined as [b]the rate of change of displacement with respect to time[/b]. Hence, the velocity function,v is given by:[br][i]Halaju didefinisikan sebagai kadar perubahan sesaran terhadap masa. Oleh itu, fungsi halaju, v, diberikan oleh:[/i][/justify][center][br][math]v=\frac{ds}{dt}[/math][br][br][/center][justify][size=100]The[b] acceleration[/b] is [b]the rate of change of velocity with respect to time[/b]. Hence, the acceleration function,a is given by:[br][i]Pecutan ialah kadar perubahan halaju terhadap masa. Oleh itu, fungsinya, a diberi oleh:[/i][br][br][/size][/justify][i][center][math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}=\frac{d^2s}{dt^2}[/math][/center][/i][justify][br]The relationship between the displacement function, s, the velocity function, v, and the acceleration function, a, can be summarized as shown in the following diagram:[br][i]Hubung kait antara fungsi sesaran, s, fungsi halaju, v, dan fungsi pecutan, a, boleh diringkaskan seperti dalam rajah yang berikut:[/i][/justify]
8.3 Pengamiran dalam Kinematik Gerakan Linear
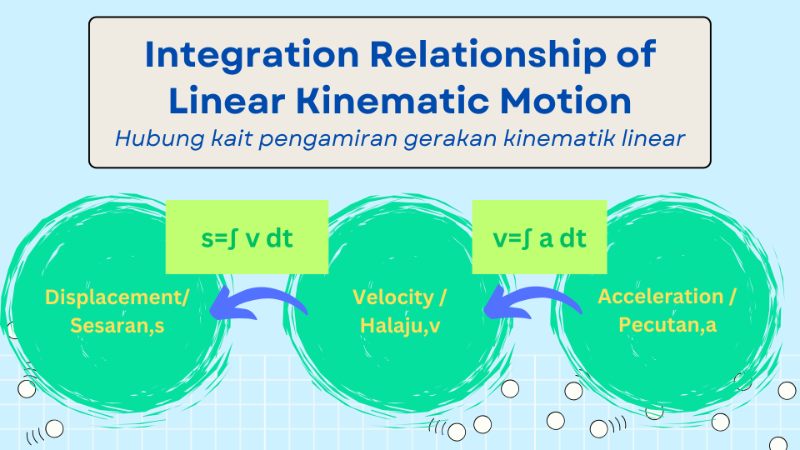
[justify]You had learnt the acceleration function, a of a particle that moves linearly can be obtained by differentiating the velocity function, v with respect to time. t, that is:[br][i]Anda telah mempelajari bahawa fungsi pecutan, a bagisuatu zarah yang bergerak secara linear ditentukan melalui pembezaan fungsi halaju, v terhadap masa, t, iaitu:[/i][br] [math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math][br][br]However, if the acceleration function, a, of a particle is given, how can we determine the velocity function,v of the particle?[br][i]Jika diberi fungsi pecutan, a bagi gerakan linear suatu zarah,apakah cara untuk menentukan fungsi halaju, v zarah tersebut?[/i][br][br]When the acceleration function [math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math], the velocity function, v can be determined by integrating the acceleration function, a with respect to time, t which is [math]v=\int a[/math]dt.[br][i][br]Apabila fungsi pecutan, a diberi, iaitu [math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math][/i][i], fungsi halaju, v boleh ditentukan dengan melakukan pengamiran fungsi pecutan, a terhadap masa t, iaitu [math]v=\int a[/math] dt.[br][br][/i]In general, the relationship between acceleration function, a = h(t) and velocity function, v = g(t) can be simplified as follows:[br][i]Secara amnya, hubungan antara fungsi pecutan a = h(t) dan fungsi halaju v = g(t) boleh diringkaskan seperti berikut.[/i][br][/justify][br] [math]a=h\left(t\right)[/math] [math]\longrightarrow[/math] [math]v=\int adt[/math] [math]\longrightarrow[/math] [math]v=g\left(t\right)[/math]
[justify]Given a velocity function, v, how can we determine the displacement, s, of the particle? How can we determine the velocity function, v, and alsoy the displacement function, s, of a particle from an acceleration function, a?[br][i]Jika diberi suatu fungsi halaju, v, bagaimanakah untuk menentukan fungsi sesaran, s, zarah itu? Bagaimanakah pula untuk menentukan fungsi halaju, v dan seterusnya fungsi sesaran, s suatu zarah daripada suatu fungsi pecutan, a?[/i][br][br]When the velocity function, v, is given as a function of time t, the displacement function, s, can be obtained by performing integration, which is:[br][i]Apabila fungsi halaju, v, diberi sebagai satu fungsi masa t, fungsi sesaran, s boleh diperoleh dengan melakukan pengamiran, iaitu[/i][br][br][b]s=∫ v dt[/b][br][br]and when the acceleration function, a, is given as a function of time t, the displacement function, s, can be obtained by performing two consecutive integrations, which are:[br][i]dan apabila fungsi pecutan, a, diberi sebagai satu fungsi masa t, fungsi sesaran, s, boleh diperoleh dengan melakukan pengamiran sebanyak dua kali secara berturut-turut,iaitu:[/i][br][/justify]
8.4 Aplikasi Kinematik Gerakan Linear
Solve linear motion kinematics problems involving differentiation and integration
[i]Menyelesaikan masalah kinematik gerakan linear yang melibatkan pembezaan dan pengamiran[/i][br][br]We have learned that the relationship between displacement, [math]s[/math], velocity, [math]v[/math] and acceleration [math]a[/math], for an object moving linearly, is as follows.[br][br][i]Kita telah mempelajari bahawa hubungan antara sesaran, [/i][math]s[/math][i], halaju, [/i][math]v[/math][i] dan pecutan, [/i][math]a[/math][i] bagi suatu objek yang bergerak secara linear adalah seperti berikut.[/i][br][br]Using differentiation[br][i]Menggunakan pembezaan[/i][br][math]v=\frac{ds}{dt},a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math][br][br]Using integration[br][i]Menggunakan pemgamiran[/i][br][math]v=\int a_{ }dt,s=\int v_{ }dt[/math][br][br]Many problems involving an object's linear motion can be solved with the knowledge and skills to apply this relationship.[br][i]Dengan pengetahuan dan kemahiran mengaplikasikan hubungan ini, banyak masalah yang melibatkan pegerakan linear suatu objek boleh diselesaikan.[/i]

LATIHAN SUMATIF SOALAN 1
Latihan Sumatif Soalan 1
A particle moves along a straight line from a fixed point O. Its displacement, s metre, at t seconds after passing O is given by [math]s=2t^3-24t^2+90t[/math]. Calculate[br][i]Suatu zarah bergerak di sepanjang satu garis lurus dari satu titik tetap O. Sesaran, s meter, zarah itu pada masa t saat selepas melalui O diberi oleh [/i][math]s=2t^3-24t^2+90t[/math][i]. Hitung[/i]
(a) the distance, in m, of the particle from the fixed point O when t=8,[br][i] sesaran, dalam meter, zarah itu dari titik tetap O apabila t=8,[/i]
(b) its velocity, in ms[sup]-1[/sup], when t=1,[br][i] halaju, dalam ms[sup]-1[/sup], apabila t=1,[/i]
(c) its acceleration, in ms[sup]-2[/sup], when t=3,[br][i] pecutan, dalam ms[sup]-2[/sup], apabila t=3,[/i]
(d) the values of t, in seconds, when the particle stops momentarily.[br][i] nilai-nilai t, dalam saat, apabila zarah itu berhenti seketika.[/i]
2020 Penang

[size=150][b]A particle P moves along a straight line and passes throuh a fixed point [/b][i]O.[/i][b]Its velocity, [/b][i]v[/i] ms[sup]-1[/sup], [b]is given by [math]v=8+2t-t^2[/math], where [/b][i]t[/i] [b]is the time, in seconds, after passing through [/b][i]O.[br][Assume motion is to the right is positive.][br][br][/i][/size][i][size=150]Sebuah zarah P bergerak sepanjang garis lurus dan melalui satu titik tetap O. Halajunya, v ms[sup]-1[/sup], diberi oleh [math]v=8+2t-t^2[/math], dengan t ialah masa, dalam saat, selepas melalui O.[br][Anggapkan pergerakan ke kanan adalah positif.][/size][br][/i][br][size=150][b]Find[br][/b][i]Cari[/i][b][br][br](a) the initial velocity, in ms[/b][sup]-1[/sup][b], of the particle,[br][/b][/size][size=150][i](a) halaju awal, dalam ms-1, zarah itu,[/i][/size]
[size=150][b](b) the maximum velocity, in ms[/b][sup]-1[/sup][b], of the particle.[br][/b][i](b) halaju maksimum, dalam ms[sup]-1[/sup], zarah itu.[/i][/size]
[size=150][b](c) the value of [/b][i]t[/i][b] at which the particle [/b][i]P[/i][b] is at instantaneous rest,[/b][/size][b][br][/b][size=150][i](c) nilai t di mana zarah P berada dalam keadaan rehat serta-merta,[/i][/size]
[size=150][b](d) the total distance, in m, travelled by particle [/b][i]P[/i][b] in the first 6 seconds after passing through [/b][i]O.[br][/i][/size][size=150](d) jumlah jarak, dalam m, yang dilalui oleh zarah P dalam 6 saat pertama selepas melalui O.[/size]
