New computational geometry problem from a romanic church
Santa Maria de Eunate romanic church. Navarra (Spain)
Some theories arise when dealing with this church. The main one is that it copy [b]The Dome Rock [/b]at Jerusalem. The place where the christians and jews believe that Abraham near take sacrifice of their son Isaac, and muslims believe that Mahoma ascend to paradise. The Dome is surrounded by two octogonal enclosures, bur in Eunate is not the case.
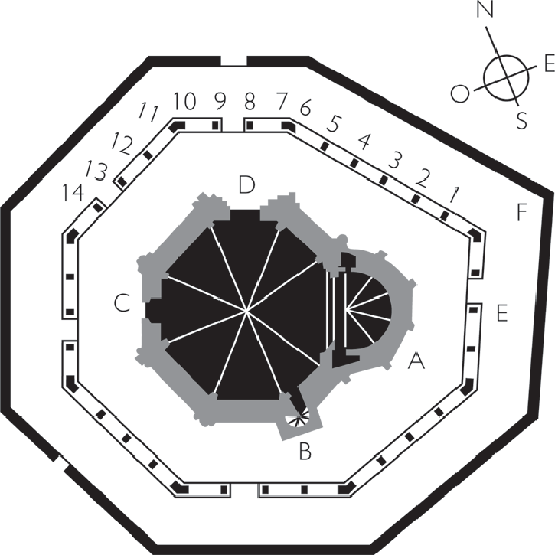
Eunate Level plan

However, we can trace the Convex Hull around the most prominent points of Eunate, af form a decagonal polygon around it. In order to achieve an octogonal one, we need to simplify this, taking the convex hull with a given number of edges (8). After we take the Convex Hull who runs parallel to the simplified one.[br][br]We make a tool [b][i]Parallel Convex Hull[/i][/b], for doing this:
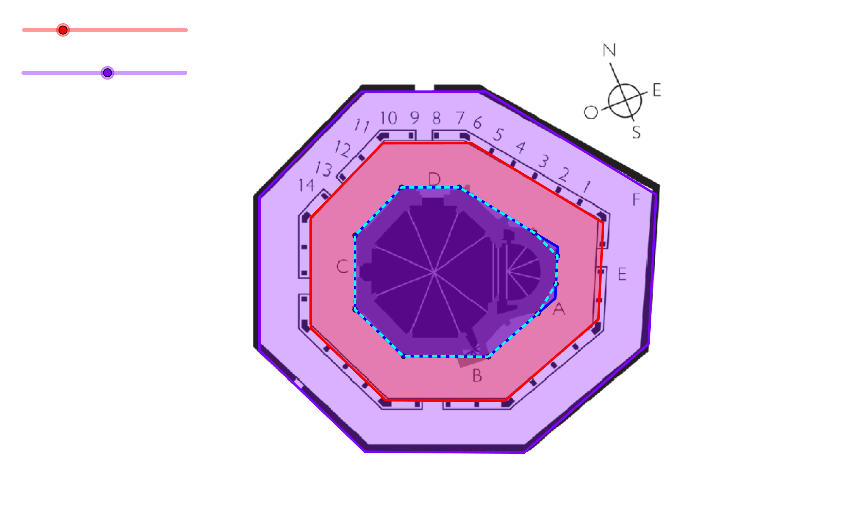
This construct a method for taking octogonal parallel enclosures (as in [b]the Dome Rock[/b]) for Eunate, based on [b][i]Parallel Convex Hull[/i][/b] and [i]Convex Hull Reduction, [/i]which fits on the level plan for Eunate.[br][br]That confirms that the church follows the Dome Rock configuration and leaves a ceremonial interpretation, as ritual walking for pilgrims to Santiago, around Eunate church. This is Aldo a burial pilgrims place for the first enclosure.