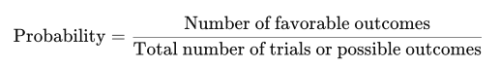
[b]Probability (確率)[/b][br][br][b]Definition:[/b][br][br]Probability is a numerical value that expresses how likely an event is to occur.[br][br][br]As the number of trials increases, the observed frequency of an outcome approaches its theoretical probability.
