
Polar Form of a Complex Number
Polar Form Representation of a Complex Number
The [color=#ff0000][b]Polar Form[/b][/color] of a complex number is written in terms of its magnitude and angle. Thus, a polar form vector is presented as: [br] [size=100][b][color=#0000ff] z= r ∠±[/color][/b][math]\phi[/math][b][color=#0000ff], [/color][/b][/size][size=100]where: [b]z[/b] is the [b]complex [/b]number in polar form, [b]r[/b] is the [b]magnitude [/b]or [b]modulo [/b]of the vector and[b] [/b][math]\phi[/math][b] [/b]is its [b]angle [/b]or argument of r. T[br][br]In polar form the location of the point is represented in a “triangular form” as shown below.[/size]
Converting between Rectangular Form and Polar Form
We can use simple geometry of the triangle and especially trigonometry and Pythagoras’s Theorem on triangles to find both the magnitude and the angle of the complex number. As we remember from school, trigonometry deals with the relationship between the sides and the angles of triangles so we can describe the relationships between the sides as:
Matrix Addition
Operations with matrices
Bearing & Trigonometric Ratios
Vertical line test
The Vertical-Line Test
Let’s now determine how we can look at a graph and decide whether it is a graph of a function. [br][b][i]A function has exactly one output for every input, [/i][/b][br]This fact means that the graph represents a function [color=#0000ff]if a vertical line could intersect the graph in more than one place.[/color]
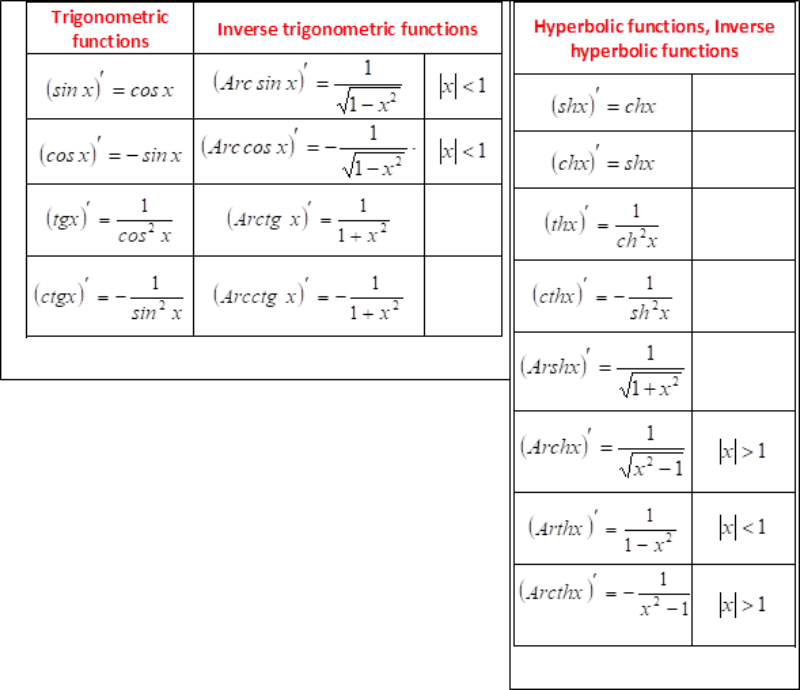
Derivation of elementary functions

Vectors
https://www.geogebra.org/m/aehmatkf
Relative frequencies of tossing 5 coins
Frequencies and relative frequencies
A table of frequencies and relative frequencies is one form of data viewing.[br]It is created for the selected variable.[br][br]The [b][color=#ff0000]frequency [/color][/b]of one category is the number of recorded values of a variable that belong to that category.[br]The [b][color=#ff0000]relative frequency[/color][/b] of a category is the frequency divided by the total number of data for that variable.[br][br]Common labels are:[br][br][list][*]frequency ⇒ [math]f[/math][/*][*]number of data of the selected variable ⇒ [math]n[/math][/*][*]relative frequency ⇒[math]\frac{f}{n}[/math][/*][/list][br]
