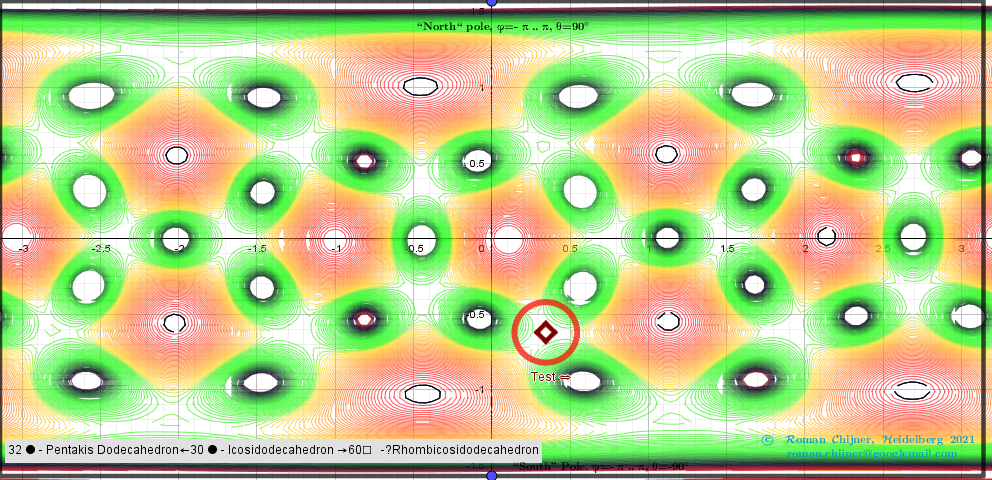
[size=85] The applet illustrates the case where 30 vertices of a [b]Icosidodecahedron[/b] "induce" the vertices of two other polyhedra:[br][b]V=32 ●[color=#ff0000]Pentakis Dodecahedron[/color]← V=30 ●[color=#0000ff]Icosidodecahedron[/color] →V=60 ☐[color=#38761d]Rhombicosidodecahedron[/color].[/b] [br]Generating polyhedra is in [url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/hymcebuw]https://www.geogebra.org/m/hymcebuw[/url]. Description are in [url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/y8dnkeuu]https://www.geogebra.org/m/y8dnkeuu[/url] and [url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/rkpxwceh]https://www.geogebra.org/m/rkpxwceh[/url]. [/size]

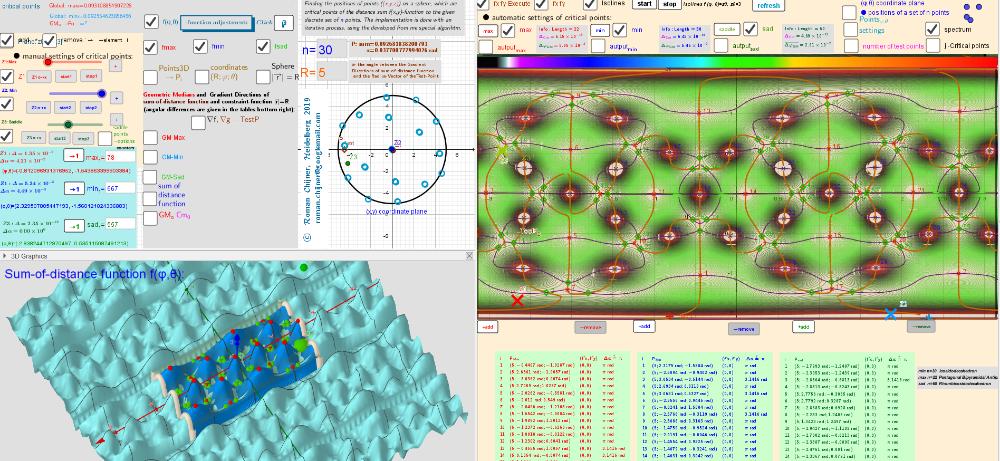
[size=85]A system of points on a sphere S of radius R “induces” on the sphere S0 of radius R0 three different sets of points, which are [color=#93c47d]geometric medians (GM)[/color] -local [color=#ff0000]maxima[/color], [color=#6d9eeb]minima[/color] and [color=#38761d]saddle[/color] points sum of distance function f(x). The angular coordinates of the spherical distribution of a system of points -[color=#0000ff] local minima[/color] coincide with the original system of points.[/size]
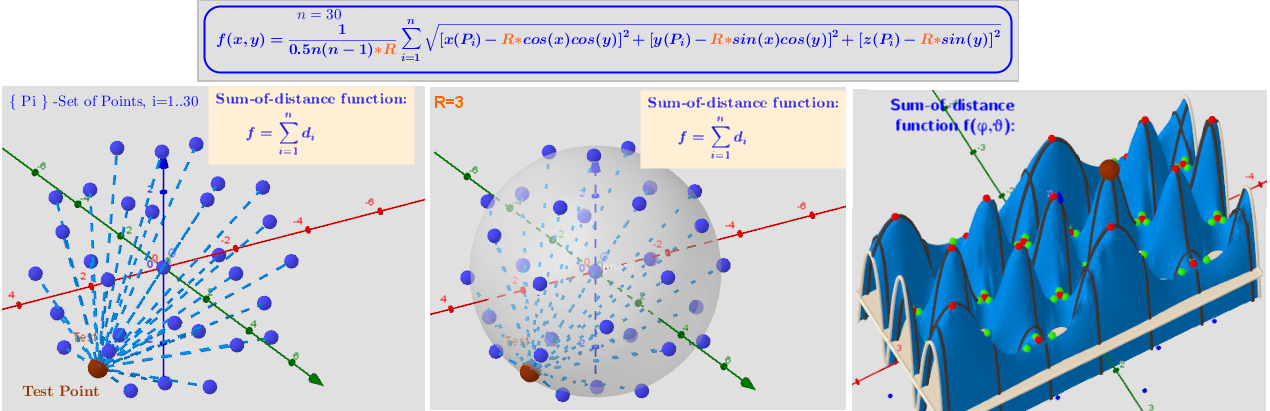
A uniform distribution of points on the surface of a sphere induces two other uniform distributions. Two-variable function f(φ,θ) over a rectangular region: - π ≤φ ≤ π; -π/2≤θ≤π/2.
[color=#333333]Distribution of points Pi[/color][color=#ff0000], [color=#5b0f00]test Point[/color], [color=#ff0000]Max[/color]/[color=#0000ff]min[/color]/[color=#38761d]saddle[/color] -[color=#333333]Critical points[/color] on a sphere. Vectors ∇f and ∇g at these points.[br]max:[/color] Pentakis Dodecahedron[br][color=#0000ff]min:[/color] Icosidodecahedron [br][color=#6aa84f]sad:[/color] Rhombicosidodecahedron(c)
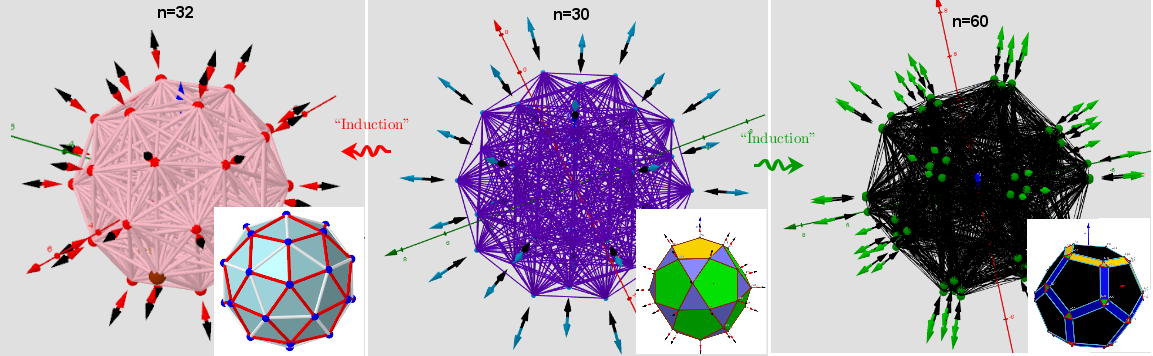
[size=85][color=#ff0000]max:[/color] Pentakis Dodecahedron[br][color=#0000ff]min:[/color] Icosidodecahedron [br][color=#6aa84f]sad:[/color] Rhombicosidodecahedron(c)[/size]
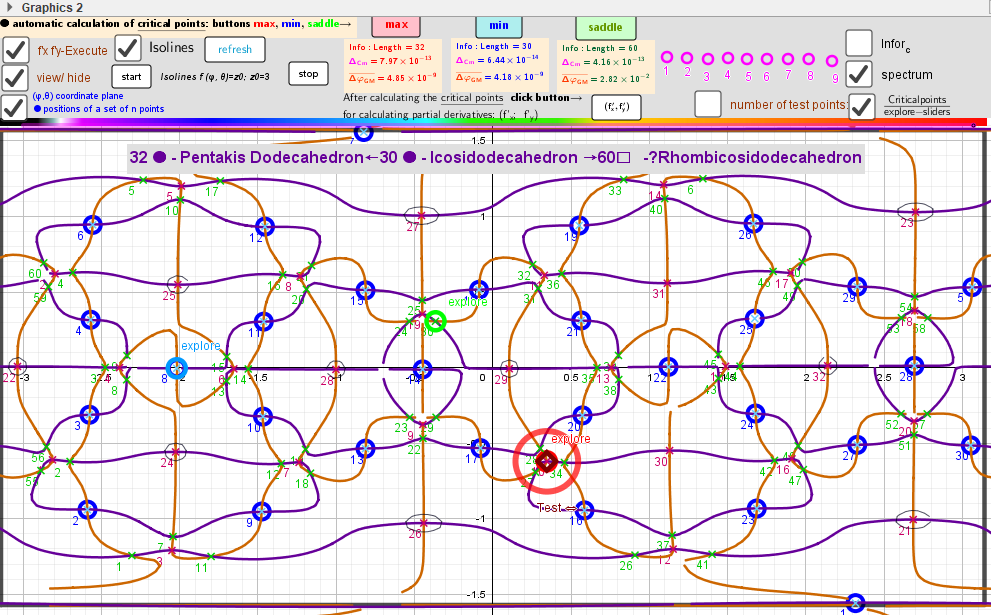
[size=85]Intersection points of implicit functions over a rectangular region: - π ≤φ ≤ π; -π/2≤θ≤π/2. A [color=#980000][b]Test[/b][/color] [b][color=#980000]point[/color][/b] -color indicator of the critical point [/size]
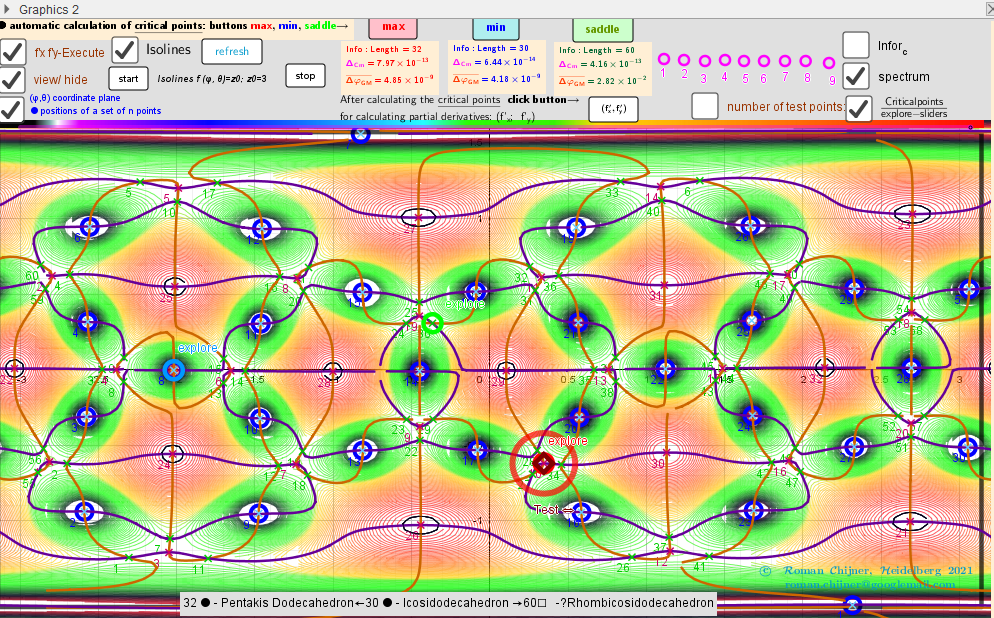
[size=85]Isolines and Intersection points of implicit functions over a rectangular region: - π ≤φ ≤ π; -π/2≤θ≤π/2.[/size]
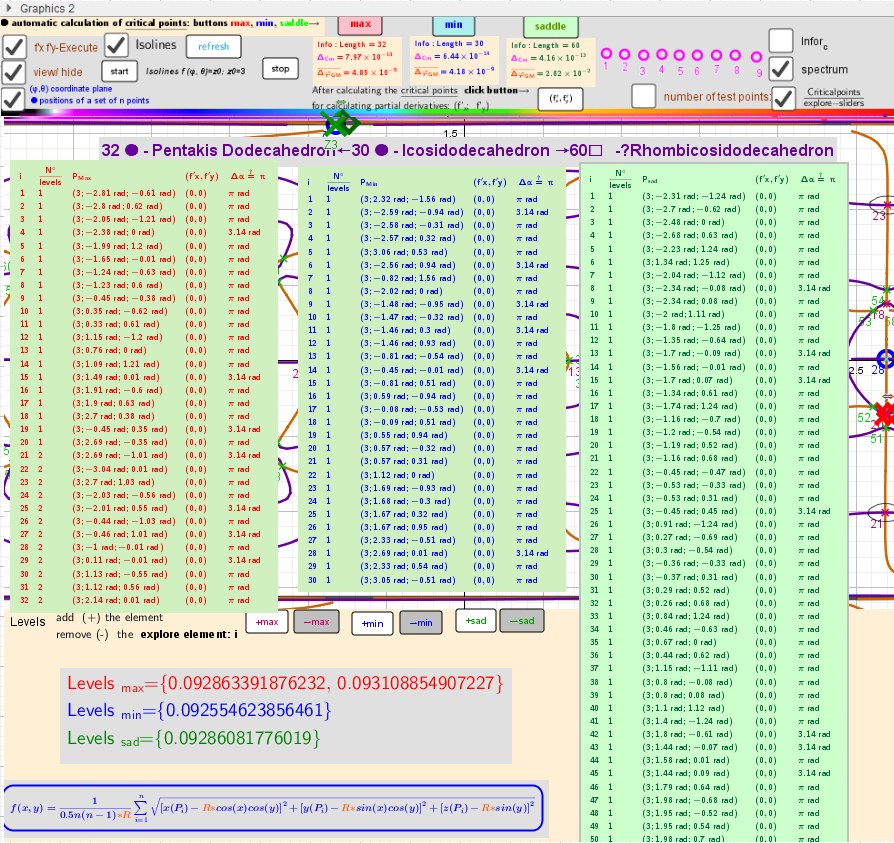
Automatic calculation of critical: [color=#ff0000]max[/color], [color=#0000ff]min[/color], [color=#6aa84f]saddle[/color] points -Solutions of the Lagrange equations.