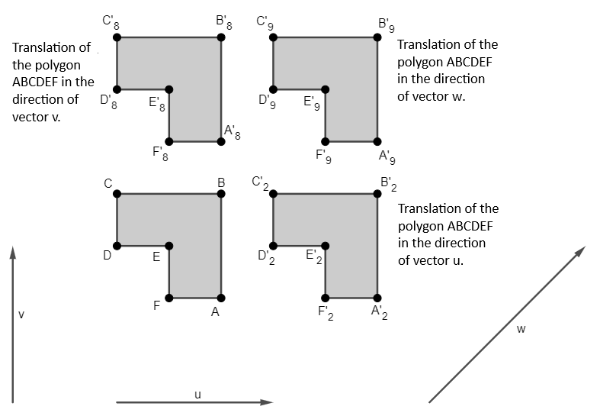
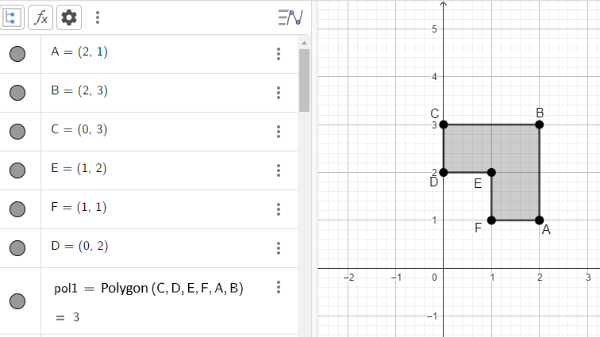
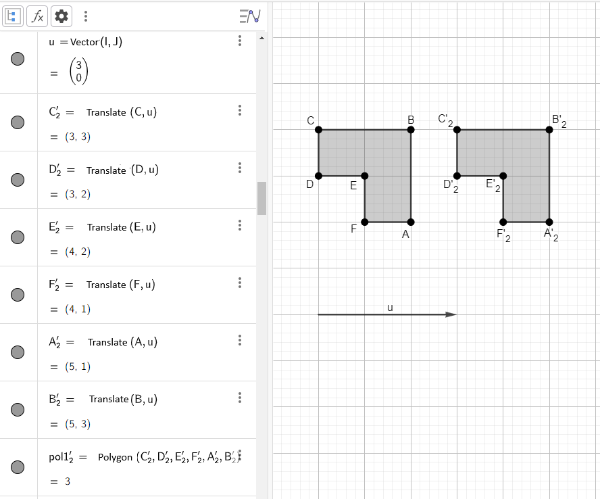
A translation is a geometric transformation that moves an object from one position to another, maintaining the same orientation and shape. In a translation, all points of the object are moved by a specific distance in a specific direction, according to a reference vector. In other words, translation moves the object without rotating or deforming it.[br][br]In Figure 1, we observe the polygon A'2B'2C'2D'2E'2F'2 resulting from the translation of the polygon ABCDEF determined by the vector u.[br][br]Other possible translations of the polygon ABCDEF can be observed in Figure 4.
In GeoGebra, the command used to perform translations is the "Translate" command when using the English version. The translation options include translating an object in the direction of a vector and translating a vector relative to a point. In this work, we will focus on the option of translating an object in relation to a vector. The translation of polygon ABCDEF in the direction of vector u is performed using the command Translate(pol1, u).[br][br]To carry out an activity involving the translation of a polygon, access the GeoGebra Geometry application through the link https://www.geogebra.org/calculator/qa7mwnfp and follow the proposed steps, which are:[br][br][br][list=1][*]Insert the points A, B, C, D, E, and F into the coordinate plane. To do so, in the input field of the Algebra window, add the points by typing ordered pairs like A = (1, 4); B = (2, 5); C = (-3, 8), etc. Alternatively, you can use the tools menu by selecting the point insertion button [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_point.png[/icon] on the toolbar and clicking on the desired location on the coordinate plane for each point you wish to insert. To rename any of the inserted points, you can right-click on the point and choose the rename option.[/*][*]Create the polygon ABCDEF using the inserted points. You can create a polygon using the command Polygon(point, ..., point) in the input field, where each of the points has the previously created coordinates, or you can draw the polygon directly on the coordinate plane using the polygon insertion button on the toolbar [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_polygon.png[/icon]. [/*][*]Create a vector u with endpoints at two arbitrary points, not necessarily the ones initially created, using the vector insertion button on the toolbar [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_vector.png[/icon]. [/*][*]Perform the translation of the polygon ABCDEF with respect to the created vector. In the input field, you can use the command Translate(object, vector), where the selected object should be the polygon ABCDEF (pol1), and the vector should be the vector u you created. Another way is to use the translation by a vector button on the toolbar [icon]/images/ggb/toolbar/mode_translatebyvector.png[/icon].[/*][/list][br]Note that, when performing the translation of polygon ABCDEF (pol1), GeoGebra will automatically translate all the points and all the segments of the polygon to generate the new polygon AB'2C'2D'2E'2F'2 (pol1'2).