Introduction
[b][size=150][size=200][color=#0000ff]What is Linear Kinematic Motion?[/color][/size][/size][/b][size=100][justify][size=150]Linear kinematic motion refers to the study of the [i]movement of objects along a straight line[/i], describing how their position, velocity, and acceleration change over time. This concept is fundamental in understanding motion in physics and is widely applied in various real-world situations, such as driving a car, objects falling freely under gravity, or the motion of projectiles.[/size][br][br][size=150][/size][size=150]Kinematics focuses on describing the motion of an object without considering the forces that cause it. In linear motion, we are particularly interested in how the following quantities interact:[br][/size][/justify][list=1][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Displacement (s):[/i][/b] The distance and direction of an object's movement from its initial position.[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Velocity (v):[/i][/b] The speed of the object in a specific direction. It can be initial velocity (u) or final velocity (v).[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Acceleration (a):[/i][/b] The rate at which the velocity changes over time.[/size][/size][/*][*][size=200][size=150][b][i]Time (t):[/i][/b] The duration of the motion.[br][/size][/size][/*][/list][br][/size]

8.1 Sesaran, Halaju dan Pecutan Sebagai Fungsi Masa

[size=200][b][color=#0000ff]What is displacement?[br][/color][/b][/size][b][color=#0000ff][size=200][i]Apakah sesaran?[/i][/size][br][/color][/b][br][size=150][b]Displacement (s)[/b] of a particle and a fixed point is the distance between the particle and the nearest fixed point measured in a certain direction.[br][i][b]Sesaran (s)[/b] bagi zarah adalah jarak antara zarah itu dengan satu titik tetap, diukur dalam arah tertentu.[br][br][/i][/size][i][color=#1e84cc][size=150][b]Here is a simpler and easier to understand way to explain the displacement, velocity and acceleration based on the direction of motion of the particle relative to the fixed point O: [/b][/size][br][/color][/i][size=150][color=#1e84cc]Berikut adalah cara yang lebih ringkas dan mudah difahami untuk menjelaskan sesaran, halaju dan pecutan berdasarkan arah gerakan zarah relatif kepada titik tetap O:[br][br][/color][/size][size=150][color=#ff0000][b]Displacement:[br][/b][b]Sesaran:[/b][/color][/size][size=150][list][*][size=150][b]Negative displacement[b] (s<0)[/b]: The particle is to the left of point O.[/b][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Sesaran negatif (s<0)[/b]: Zarah berada di [b]sebelah kiri titik O[/b].[br][br][/i][list][*][size=150][b]Zero displacement[b] (s=0): The particle is exactly at point O.[/b][/b][i][br][/i][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Sesaran sifar (s=0)[/b]: Zarah berada [b]tepat di titik O[/b].[br][/i][br][list][*][size=150][b]Positive displacement (s>0): The particle is to the right of point O.[/b][br][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Sesaran positif (s>0)[/b]: Zarah berada di [b]sebelah kanan titik O.[br][br][br][/b][/i][/size][justify][color=#ff0000][b][/b][size=150][b]Velocity:[br][/b][b]Halaju:[/b][/size][b][/b][/color][/justify][size=150][i][list][*][size=150][b]Negative velocity[b] (v<0)[/b]: The particle moves to the left.[/b][/size][/*][/list] [b]Halaju negatif (v<0)[/b][i]: [/i]Zarah bergerak [b]ke arah kiri[/b][i].[br][br][/i][list][*][size=150][b]Zero [b]velocity [/b][b](v=0): Zarah berada dalam keadaan [b]pegun[/b] (tidak bergerak).[/b][/b][i][br][/i][/size][/*][/list] [b][i][i][b]Halaju [/b][/i][/i]sifar (v=0)[/b][i]: [/i]The particle is [b]at rest (not moving)[/b][i].[br][/i][br][list][*][size=150][b]Positive velocity (v>0): Zarah bergerak ke arah kanan[/b][br][/size][/*][/list] [i][b]Halaju positif (v>0)[/b]: Zarah bergerak [b]ke arah kanan.[br][br][br][/b][/i][/i][/size][size=150][color=#ff0000][b]Acceleration:[br][/b][b][i]Pecutan[/i]:[br][/b][/color][/size][i][list][*][b][size=150]Negative acceleration[b] (a<0)[/b]: The particle's velocity is [b]increasing[/b] over time (the particle is speeding up).[/size][/b][/*][/list][size=150] [b]Pecutan negatif (v<0)[/b][i]: [/i]Halaju zarah [b]berkurang[/b] dengan masa (zarah semakin perlahan).[list][*][b]Zero [b]acceleration[/b][b](v=0): The particle's velocity is [b]constant[/b] (either at its maximum or minimum).[/b][/b][i][br][/i][/*][/list] [b][i][size=150][b]Pecutan [/b][/size][/i]sifar (v=0)[/b][i]: [/i]Halaju zarah adalah [b]tetap[/b] (maksimum atau minimum).[br][/size][/i][i][size=150][br][list][*][i][size=150][b]Positive acceleration[b] (a>0)[/b]: The particle's velocity is [b]decreasing[/b] over time (the particle is slowing down). [/b][/size][/i][/*][/list][/size][/i][i][size=150][b] Pecutan positif (a>0)[/b][i]: [/i]Halaju zarah [b]meningkat[/b] dengan masa (zarah semakin laju).[/size][/i]
8.2 Differentiations in Kinematics of Linear Motion
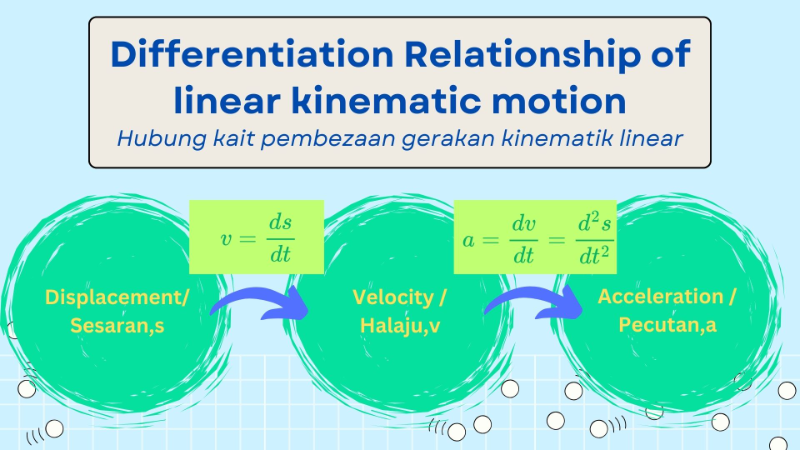
[justify][size=100]Differentiation in linear kinetic motion refers to the mathematical process of determining the rate of change of motion-related quantities, such as displacement, velocity, and acceleration, with respect to time. These rates are foundational in understanding the dynamics of objects in linear motion.[b] The differentiation always starts from displacement, s=f(x). [/b][/size][i][size=100][br][br][/size][/i]The [b]velocity[/b] is defined as [b]the rate of change of displacement with respect to time[/b]. Hence, the velocity function,v is given by:[/justify][center][br][math]v=\frac{ds}{dt}[/math][br][br][/center][justify][size=100]The[b] acceleration[/b] is [b]the rate of change of velocity with respect to time[/b]. Hence, the acceleration function,a is given by:[br][/size][/justify][i][center][math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}=\frac{d^2s}{dt^2}[/math][/center][/i][justify][br]The relationship between the displacement function, s, the velocity function, v, and the acceleration function, a, can be summarized as shown in the following diagram:[/justify]
8.3 Pengamiran dalam Kinematik Gerakan Linear
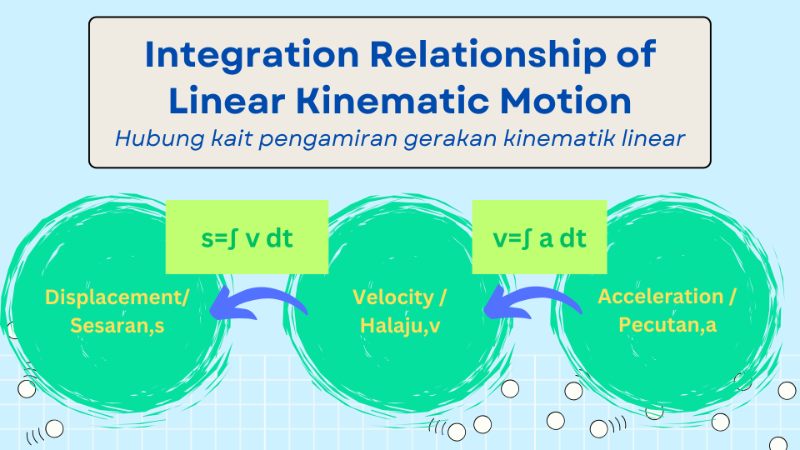
[justify]You had learnt the acceleration function, a of a particle that moves linearly can be obtained by differentiating the velocity function, v with respect to time. t, that is:[br][i]Anda telah mempelajari bahawa fungsi pecutan, a bagisuatu zarah yang bergerak secara linear ditentukan melalui pembezaan fungsi halaju, v terhadap masa, t, iaitu:[/i][br] [math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math][br][br]However, if the acceleration function, a, of a particle is given, how can we determine the velocity function,v of the particle?[br][i]Jika diberi fungsi pecutan, a bagi gerakan linear suatu zarah,apakah cara untuk menentukan fungsi halaju, v zarah tersebut?[/i][br][br]When the acceleration function [math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math], the velocity function, v can be determined by integrating the acceleration function, a with respect to time, t which is [math]v=\int a[/math]dt.[br][i][br]Apabila fungsi pecutan, a diberi, iaitu [math]a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math][/i][i], fungsi halaju, v boleh ditentukan dengan melakukan pengamiran fungsi pecutan, a terhadap masa t, iaitu [math]v=\int a[/math] dt.[br][br][/i]In general, the relationship between acceleration function, a = h(t) and velocity function, v = g(t) can be simplified as follows:[br][i]Secara amnya, hubungan antara fungsi pecutan a = h(t) dan fungsi halaju v = g(t) boleh diringkaskan seperti berikut.[/i][br][/justify][br] [math]a=h\left(t\right)[/math] [math]\longrightarrow[/math] [math]v=\int adt[/math] [math]\longrightarrow[/math] [math]v=g\left(t\right)[/math]
[justify]Given a velocity function, v, how can we determine the displacement, s, of the particle? How can we determine the velocity function, v, and alsoy the displacement function, s, of a particle from an acceleration function, a?[br][i]Jika diberi suatu fungsi halaju, v, bagaimanakah untuk menentukan fungsi sesaran, s, zarah itu? Bagaimanakah pula untuk menentukan fungsi halaju, v dan seterusnya fungsi sesaran, s suatu zarah daripada suatu fungsi pecutan, a?[/i][br][br]When the velocity function, v, is given as a function of time t, the displacement function, s, can be obtained by performing integration, which is:[br][i]Apabila fungsi halaju, v, diberi sebagai satu fungsi masa t, fungsi sesaran, s boleh diperoleh dengan melakukan pengamiran, iaitu[/i][br][br][b]s=∫ v dt[/b][br][br]and when the acceleration function, a, is given as a function of time t, the displacement function, s, can be obtained by performing two consecutive integrations, which are:[br][i]dan apabila fungsi pecutan, a, diberi sebagai satu fungsi masa t, fungsi sesaran, s, boleh diperoleh dengan melakukan pengamiran sebanyak dua kali secara berturut-turut,iaitu:[/i][br][/justify]
8.4 Aplikasi Kinematik Gerakan Linear
Solve linear motion kinematics problems involving differentiation and integration
[i]Menyelesaikan masalah kinematik gerakan linear yang melibatkan pembezaan dan pengamiran[/i][br][br]We have learned that the relationship between displacement, [math]s[/math], velocity, [math]v[/math] and acceleration [math]a[/math], for an object moving linearly, is as follows.[br][br][i]Kita telah mempelajari bahawa hubungan antara sesaran, [/i][math]s[/math][i], halaju, [/i][math]v[/math][i] dan pecutan, [/i][math]a[/math][i] bagi suatu objek yang bergerak secara linear adalah seperti berikut.[/i][br][br]Using differentiation[br][i]Menggunakan pembezaan[/i][br][math]v=\frac{ds}{dt},a=\frac{dv}{dt}[/math][br][br]Using integration[br][i]Menggunakan pemgamiran[/i][br][math]v=\int a_{ }dt,s=\int v_{ }dt[/math][br][br]Many problems involving an object's linear motion can be solved with the knowledge and skills to apply this relationship.[br][i]Dengan pengetahuan dan kemahiran mengaplikasikan hubungan ini, banyak masalah yang melibatkan pegerakan linear suatu objek boleh diselesaikan.[/i]

LATIHAN SUMATIF SOALAN 1
Latihan Sumatif Soalan 1
A particle moves along a straight line from a fixed point O. Its displacement, s metre, at t seconds after passing O is given by [math]s=2t^3-24t^2+90t[/math]. Calculate[br][i]Suatu zarah bergerak di sepanjang satu garis lurus dari satu titik tetap O. Sesaran, s meter, zarah itu pada masa t saat selepas melalui O diberi oleh [/i][math]s=2t^3-24t^2+90t[/math][i]. Hitung[/i]
(a) the distance, in m, of the particle from the fixed point O when t=8,[br][i] sesaran, dalam meter, zarah itu dari titik tetap O apabila t=8,[/i]
(b) its velocity, in ms[sup]-1[/sup], when t=1,[br][i] halaju, dalam ms[sup]-1[/sup], apabila t=1,[/i]
(c) its acceleration, in ms[sup]-2[/sup], when t=3,[br][i] pecutan, dalam ms[sup]-2[/sup], apabila t=3,[/i]
(d) the values of t, in seconds, when the particle stops momentarily.[br][i] nilai-nilai t, dalam saat, apabila zarah itu berhenti seketika.[/i]
2020 Penang

[size=150][b]A particle P moves along a straight line and passes throuh a fixed point [/b][i]O.[/i][b]Its velocity, [/b][i]v[/i] ms[sup]-1[/sup], [b]is given by [math]v=8+2t-t^2[/math], where [/b][i]t[/i] [b]is the time, in seconds, after passing through [/b][i]O.[br][Assume motion is to the right is positive.][br][/i][/size][br][size=150][b]Find[/b][b][br][br](a) the initial velocity, in ms[/b][sup]-1[/sup][b], of the particle,[/b][/size]
[size=150][b](b) the maximum velocity, in ms[/b][sup]-1[/sup][b], of the particle.[br][/b][/size]
[size=150][b](c) the value of [/b][i]t[/i][b] at which the particle [/b][i]P[/i][b] is at instantaneous rest,[/b][/size]
[size=150][b](d) the total distance, in m, travelled by particle [i]P[/i] in the first 6 seconds after passing through [/b][i][b]O.[/b][br][/i][/size]
