WEIERSTRASSsche ℘ - Funktion
[right][size=85][size=50][size=50]Diese Seite ist Teil des [color=#980000][i][b]GeoGebra-Books[/b][/i][/color] [url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/kCxvMbHb]Moebiusebene[/url]. [color=#ff7700][b](20.01.2023)[br][/b][/color][/size][/size][/size][size=85][size=50][size=50][color=#ff7700][color=#000000]Kapitel: [color=#0000ff]"[url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/kCxvMbHb#chapter/409348][i][b]Spezielle komplexe Funktionen[/b][/i][/url][/color]"[/color][/color][/size][/size][/size][/right]
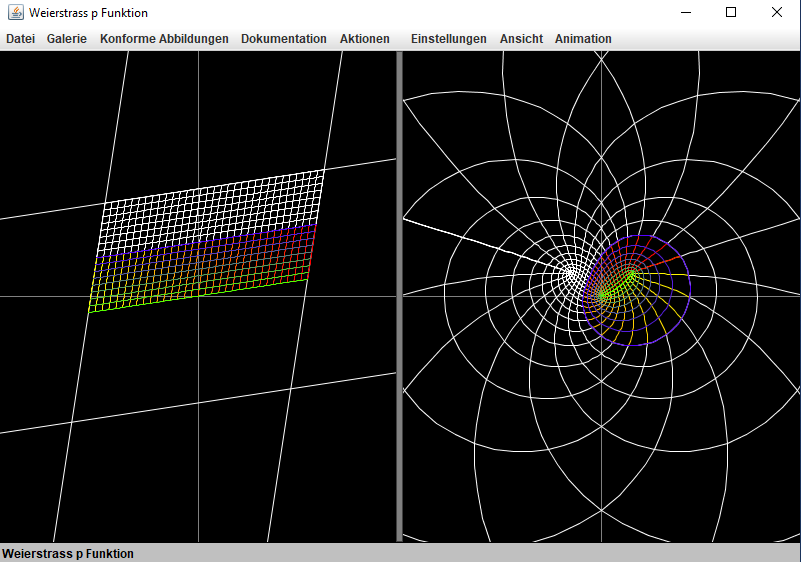
[size=85]Das[/size][size=85] Applet zeigt [math]x=\mathbf{const}[/math], bzw. [math]y=\mathbf{const}[/math] Kurven der [color=#9900ff][i][b]elliptischen[/b][/i][/color] [b]WEIERSTRASS[/b]schen [math]\wp[/math]-[color=#38761D][i][b]Funktion[/b][/i][/color] [math]x+i\cdot y=z\mapsto g(z)[/math][br]mit den [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkten[/b][/i][/color] [math]f_{-1}=-1[/math], [math]f_0=0[/math] und [math]f[/math] auf der [math]x[/math]-Achse. Der 4.-te [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkt[/b][/i][/color] ist [math]\infty[/math].[br]Es handelt sich um [i][b]Kartesische Ovale[/b][/i], benannt nach [b]RENÈ DESCARTES.[/b][br]Die [color=#9900ff][i][b]elliptische Differentialgleichung[/b][/i][/color] dieser [math]\wp[/math]-[/size][size=85][color=#38761D][i][b]Funktion[/b][/i][/color][/size][size=85] ist[/size][list][*][math]\left(g'\right)=\left(g+1\right)\cdot\left(g-0\right)\cdot\left(g-f\right)[/math][/*][/list][size=85]Die [color=#38761D][i][b]WEIERSTRASSsche [math]\wp[/math]-Funktion[/b][/i][/color] ist in [color=#980000][b]geogebra[/b][/color] nicht implementiert.[br]Die [color=#ff7700][i][b]Kurven[/b][/i][/color] werden als [i][b]implizite Kurven[/b][/i] mit [color=#ff7700][i][b]bizirkularen Quartik[/b][/i][/color]-Gleichungen gezeichnet. [br][br]Jede [color=#9900ff][i][b]elliptische Funktion[/b][/i][/color] mit [color=#cc0000][b]4[/b][/color] verschiedenen [color=#ff0000][i][b]konzyklischen[/b][/i][/color] [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkten[/b][/i][/color] läßt sich mittels einer[br]geeigneten [color=#0000ff][i][b]Möbiustransformation[/b][/i][/color] durch eine [b]WEIERSRASS[/b]sche [math]\wp[/math]-Funktion des obigen Typs darstellen:[br][color=#cc0000][b]3[/b][/color] der [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkte[/b][/i][/color] bilde man auf [math]\infty,-1,0[/math] ab, der [color=#cc0000][b]4.[/b][/color] [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkt[/b][/i][/color] ist dann frei beweglich.[br][br]Das Bild unten zeigt eine [b]WEIERSTRASS[/b]sche [math]\wp[/math]-[/size][size=85][color=#38761D][i][b]Funktion[/b][/i][/color][/size][size=85], deren [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkte[/b][/i][/color] nicht [color=#ff0000][i][b]konzyklisch[/b][/i][/color] sind [br]- dh: Die [color=#00ff00][i][b]Brennpunkte[/b][/i][/color] liegen nicht mit [math]\infty[/math] auf einer [color=#ff0000][i][b]Geraden[/b][/i][/color]! [br]Die deutlich zu erkennenden geschlossenen [i][b]Kurven[/b][/i] sind [color=#0000ff][i][b]nicht algebraisch[/b][/i][/color], also insbesondere keine [color=#ff7700][i][b]bizirkularen Quartiken[/b][/i][/color].[br]Die [i][b]Kurven[/b][/i] besitzen keinen [color=#f1c232][i][b]Symmetrie-Kreis[/b][/i][/color].[br][br]Das Bild ist enthalten in der [i]Bilder-Galerie[/i] der [b]3D-XPLOR_J[/b]-Application.[/size]

[size=85][i][b]Kartesische Ovale[/b][/i] erlauben die Konstruktion von [color=#ff7700][i][b]6-Eck-Netzen[/b][/i][/color] aus [color=#ff0000][i][b]Kreisen[/b][/i][/color], [br]siehe [math]\hookrightarrow[/math] [url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/kCxvMbHb#material/Tg8ZXDvF][color=#0000ff][u][i][b]Cartesisches Oval mit endlichem Kreis-6-Ecknetz[/b][/i][/u][/color][/url][/size]