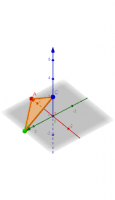
This demo shows how the Pythagorean theorem can be generalized from 2D to 3D, where the area of a polygon ABC can be computed from the areas of polygons OAB, OBC and OAC (where O is the origin and points A, B and C are on the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis respectively) analogous to the way the length of the hypotenuse can be computed from the lengths of the other two sides of a right triangle.